SLC6 transporters: structure, function, regulation, disease association and therapeutics
- PMID: 23506866
- PMCID: PMC3602807
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mam.2012.07.002
SLC6 transporters: structure, function, regulation, disease association and therapeutics
Abstract
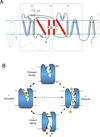
The SLC6 family of secondary active transporters are integral membrane solute carrier proteins characterized by the Na(+)-dependent translocation of small amino acid or amino acid-like substrates. SLC6 transporters, which include the serotonin, dopamine, norepinephrine, GABA, taurine, creatine, as well as amino acid transporters, are associated with a number of human diseases and disorders making this family a critical target for therapeutic development. In addition, several members of this family are directly involved in the action of drugs of abuse such as cocaine, amphetamines, and ecstasy. Recent advances providing structural insight into this family have vastly accelerated our ability to study these proteins and their involvement in complex biological processes.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures




References
-
- Accardi A, Miller C. Secondary active transport mediated by a prokaryotic homologue of ClC Cl-channels. Nature. 2004;427:803–807. - PubMed
-
- Adkins EM, Samuvel DJ, Fog JU, Eriksen J, Jayanthi LD, Vaegter CB, Ramamoorthy S, Gether U. Membrane mobility and microdomain association of the dopamine transporter studied with fluorescence correlation spectroscopy and fluorescence recovery after photobleaching. Biochemistry. 2007;46:10484–10497. - PubMed
-
- Agoston GE, Vaughan R, Lever JR, Izenwasser S, Terry PD, Newman AH. A novel photoaffinity label for the dopamine transporter based on N-substituted 3 -[bis(4'-fluorophenyl)methoxy]tropane. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 1997;7:3027–3032.
-
- Amara SG, Sonders MS. Neurotransmitter transporters as molecular targets for addictive drugs. Drug Alcohol Depend. 1998;51:87–96. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

