The SLCO (former SLC21) superfamily of transporters
- PMID: 23506880
- PMCID: PMC3602805
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mam.2012.10.009
The SLCO (former SLC21) superfamily of transporters
Abstract
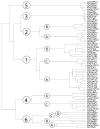
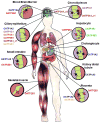
The members of the organic anion transporting polypeptide superfamily (OATPs) are classified within the SLCO solute carrier family. All functionally well characterized members are predicted to have 12 transmembrane domains and are sodium-independent transport systems that mediate the transport of a broad range of endo- as well as xenobiotics. Substrates are mainly amphipathic organic anions with a molecular weight of more than 300Da, but some of the known transported substrates are also neutral or even positively charged. Among the well characterized substrates are numerous drugs including statins, angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors, angiotensin receptor blockers, antibiotics, antihistaminics, antihypertensives and anticancer drugs. Based on their amino acid sequence identities, the different OATPs cluster into families (in general with more than 40% amino acid sequence identity) and subfamilies (more than 60% amino acid identity). With the sequencing of genomes from different species and the computerized prediction of encoded proteins more than 300 OATPs can be found in the databases, however only a fraction of them have been identified in humans, rodents, and some additional species important for pharmaceutical research like the rhesus monkey (Macaca mulatta), the dog (Canis lupus familiaris) and the pig (Sus scrofa). These OATPs form 6 families (OATP1-OATP6) and 13 subfamilies. In this review we try to summarize what is currently known about OATPs with respect to endogenous substrates, tissue distribution, transport mechanisms, regulation of expression, structure-function relationship and mutations and polymorphisms.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Abe T, Kakyo M, Tokui T, Nakagomi R, Nishio T, Nakai D, Nomura H, Unno M, Suzuki M, Naitoh T, Matsuno S, Yawo H. Identification of a novel gene family encoding human liver-specific organic anion transporter LST-1. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:17159–17163. - PubMed
-
- Abe T, Unno M, Onogawa T, Tokui T, Kondo TN, Nakagomi R, Adachi H, Fujiwara K, Okabe M, Suzuki T, Nunoki K, Sato E, Kakyo M, Nishio T, Sugita J, Asano N, Tanemoto M, Seki M, Date F, Ono K, Kondo Y, Shiiba K, Suzuki M, Ohtani H, Shimosegawa T, Iinuma K, Nagura H, Ito S, Matsuno S. LST-2, a human liver-specific organic anion transporter, determines methotrexate sensitivity in gastrointestinal cancers. Gastroenterology. 2001;120 (7):1689–1699. - PubMed
-
- Adachi H, Suzuki T, Abe M, Asano N, Mizutamari H, Tanemoto M, Nishio T, Onogawa T, Toyohara T, Kasai S, Satoh F, Suzuki M, Tokui T, Unno M, Shimosegawa T, Matsuno S, Ito S, Abe T. Molecular characterization of human and rat organic anion transporter OATP-D. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2003;285 (6):F1188–1197. - PubMed
-
- Alkemade A, Friesema EC, Kalsbeek A, Swaab DF, Visser TJ, Fliers E. Expression of thyroid hormone transporters in the human hypothalamus. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2011;96 (6):E967–971. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

