Deficit of p66ShcA restores redox-sensitive stress response program in cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury
- PMID: 23506954
- PMCID: PMC3720132
- DOI: 10.1016/j.yexmp.2013.03.001
Deficit of p66ShcA restores redox-sensitive stress response program in cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury
Abstract
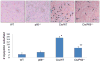
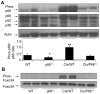
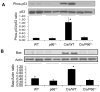
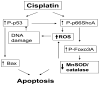
Overwhelming oxidative stress and compromised tubular cell antioxidant response have been incriminated for cisplatin (Cis)-induced acute kidney injury (AKI). We hypothesized that Cis-induced AKI was the outcome of the deactivated redox-sensitive stress response program (RSSRP). Wild type (WT) and heterozygous p66ShcA(p66(+/-)) mice in groups of six were administered either normal saline (WT) or Cis (12.5 mg/kg, intraperitoneal, Cis/WT). Renal biomarkers were collected and kidneys were harvested for renal histology. Cis/WT showed elevated blood urea nitrogen levels and enhanced tubular cell apoptosis, necrosis, and dilated tubules filled with casts when compared to Cis/p66(+/-). Cis/p66(+/-) developed only a clinically occult AKI (normal blood urea levels and only microscopic alterations). Immunoblots from the lysates of renal tissues of Cis/WT displayed enhanced expression of phospho-p66ShcA, and phospho-Foxo3A but attenuated expression of MnSOD and catalase; conversely, p66 deficit prevented these alterations in Cis milieu. In in vitro studies, Cis treated mouse proximal tubular cells (MPTCs) displayed enhanced phosphorylation of p66ShcA and no increase in tubular cell expression of MnSOD. In addition, renal tissues of Cis/WT and Cis-treated MPTCs displayed enhanced phosphorylation of p53 and Bax expression. However, MPTC partially silenced for p66ShcA displayed partial inhibition of Cis-induced tubular cell apoptosis as well as necrosis. These findings indicate that Cis-induced AKI is the outcome of the deactivated RSSRP (attenuated anti-oxidant response) and activation of pro-apoptotic (p53-induced Bax expression) pathway.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures






References
-
- Arany I, Safirstein RL. Cisplatin nephrotoxicity. Semin Nephrol. 2003;23:460–464. - PubMed
-
- Baliga R, Zhang Z, Baliga M, Ueda N, Shah SV. In vitro and in vivo evidence suggesting a role for iron in cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity. Kidney Int. 1998;53:394–401. - PubMed
-
- Camici GG, Schiavoni M, Francia P, Bachschmid M, Martin-Padura I, Hersberger M, Tanner FC, Pelicci P, Volpe M, Anversa P, Luscher TF, Cosentino F. Genetic deletion of p66(Shc) adaptor protein prevents hyperglycemia-induced endothelial dysfunction and oxidative stress. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2007;104:5217–5222. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chintapalli J, Yang S, Opawumi D, Goyal SR, Shamsuddin N, Malhotra A, Reiss K, Meggs LG. Inhibition of wild-type p66ShcA in mesangial cells prevents glycooxidant-dependent FOXO3a regulation and promotes the survival phenotype. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2007;292:F523–530. - PubMed
-
- Clark JS, Faisal A, Baliga R, Nagamine Y, Arany I. Cisplatin induces apoptosis through the ERK-p66shc pathway in renal proximal tubule cells. Cancer Lett. 2010;297:165–70. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

