Advances in CKD detection and determination of prognosis: executive summary of the National Kidney Foundation-Kidney Early Evaluation Program (KEEP) 2012 annual data report
- PMID: 23507265
- PMCID: PMC3608929
- DOI: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2013.01.006
Advances in CKD detection and determination of prognosis: executive summary of the National Kidney Foundation-Kidney Early Evaluation Program (KEEP) 2012 annual data report
Figures
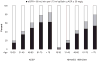

Similar articles
-
National Kidney Foundation's Kidney Early Evaluation Program (KEEP) annual data report 2010: executive summary.Am J Kidney Dis. 2011 Mar;57(3 Suppl 2):S1-3. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2010.11.011. Am J Kidney Dis. 2011. PMID: 21338845 No abstract available.
-
KEEP plants the seeds for prevention.Nephrol News Issues. 2012 Apr;26(4):8. Nephrol News Issues. 2012. PMID: 22558718 No abstract available.
-
Longitudinal analysis of participants in the KEEP Mexico's chronic kidney disease screening program.Arch Med Res. 2013 Nov;44(8):650-4. doi: 10.1016/j.arcmed.2013.10.006. Epub 2013 Nov 8. Arch Med Res. 2013. PMID: 24211753 Clinical Trial.
-
[What do we know about chronic kidney disease at the beginning of the 21st century?].Acta Med Croatica. 2014 Apr;68(2):75-7. Acta Med Croatica. 2014. PMID: 26012141 Review. Croatian.
-
Chronic kidney disease epidemic: How do we deal with it?Nephrology (Carlton). 2018 Oct;23 Suppl 4:116-120. doi: 10.1111/nep.13464. Nephrology (Carlton). 2018. PMID: 30298662 Review.
Cited by
-
Cardiovascular safety outcomes of once-weekly GLP-1 receptor agonists in people with type 2 diabetes.J Clin Pharm Ther. 2020 Sep;45 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):61-72. doi: 10.1111/jcpt.13226. J Clin Pharm Ther. 2020. PMID: 32910492 Free PMC article. Review.
-
High Prevalence and Low Awareness of Albuminuria in the Community Setting in the KDSAP.Kidney Int Rep. 2019 Dec 27;5(4):475-484. doi: 10.1016/j.ekir.2019.12.011. eCollection 2020 Apr. Kidney Int Rep. 2019. PMID: 32280843 Free PMC article.
-
Potential approaches to reverse or repair renal fibrosis.Nat Rev Nephrol. 2014 Apr;10(4):226-37. doi: 10.1038/nrneph.2014.14. Epub 2014 Feb 11. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2014. PMID: 24514753 Review.
-
Creatinine Assay Attainment of Analytical Performance Goals Following Implementation of IDMS Standardization: Further Improvements Required.Can J Kidney Health Dis. 2017 Feb 23;4:2054358117693353. doi: 10.1177/2054358117693353. eCollection 2017. Can J Kidney Health Dis. 2017. PMID: 28321322 Free PMC article.
-
United States Renal Data System public health surveillance of chronic kidney disease and end-stage renal disease.Kidney Int Suppl (2011). 2015 Jun;5(1):2-7. doi: 10.1038/kisup.2015.2. Kidney Int Suppl (2011). 2015. PMID: 26097778 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Moyer VA. Screening for chronic kidney disease: US Preventive Services Task Force recommendation statement. Ann Intern Med. 2012;157(8):567–570. - PubMed
-
- Stevens LA, Li S, Kurella Tamura M, Chen SC, Vassalotti JA, Norris KC, Whaley-Connell AT, Bakris GL, McCullough PA, et al. Comparison of the Chronic Kidney Disease Epidemiology Collaboration and Modification of Diet in Renal Disease Study glomerular filtration rate estimating equations for determining chronic kidney disease prevalence, risk factors and mortality in the Kidney Early Evaluation Program. Am J Kidney Dis. 2011;57(Suppl 2):S9–S16. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Whaley-Connell AT, Sowers JR, Stevens LA, McFarlane SI, Shlipak MG, Norris KC, Chen SC, Qiu Y, Wang C, Li S, Vassalotti JA, Collins AJ Kidney Early Evaluation Program Investigators et al. CKD in the United States: Kidney Early Evaluation Program (KEEP) and National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) 1999–2004. Am J Kidney Dis. 2008;51(Suppl 2):S13–S20. - PubMed
-
- McCullough PA, Jurkovitz CT, Pergola PE, McGill JB, Brown WW, Collins AJ, Chen SC, Li S, Singh A, Norris KC, Klag MJ, Bakris GL for the KEEP Investigators. Independent components of chronic kidney disease as a cardiovascular risk state: results from the Kidney Early Evaluation Program (KEEP) Arch Intern Med. 2007;167(11):1122–1129. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

