Development and use of the generic WHO/CDC logic model for vitamin and mineral interventions in public health programmes
- PMID: 23507463
- PMCID: PMC4547471
- DOI: 10.1017/S1368980013000554
Development and use of the generic WHO/CDC logic model for vitamin and mineral interventions in public health programmes
Abstract
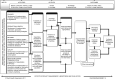
Objective: Nutrition interventions are critical to achieve the Millennium Development Goals; among them, micronutrient interventions are considered cost-effective and programmatically feasible to scale up, but there are limited tools to communicate the programme components and their relationships. The WHO/CDC (Centers for Disease Control and Prevention) logic model for micronutrient interventions in public health programmes is a useful resource for planning, implementation, monitoring and evaluation of these interventions, which depicts the programme theory and expected relationships between inputs and expected Millennium Development Goals.
Design: The model was developed by applying principles of programme evaluation, public health nutrition theory and programmatic expertise. The multifaceted and iterative structure validation included feedback from potential users and adaptation by national stakeholders involved in public health programmes' design and implementation.
Results: In addition to the inputs, main activity domains identified as essential for programme development, implementation and performance include: (i) policy; (ii) products and supply; (iii) delivery systems; (iv) quality control; and (v) behaviour change communication. Outputs encompass the access to and coverage of interventions. Outcomes include knowledge and appropriate use of the intervention, as well as effects on micronutrient intake, nutritional status and health of target populations, for ultimate achievement of the Millennium Development Goals.
Conclusions: The WHO/CDC logic model simplifies the process of developing a logic model by providing a tool that has identified high-priority areas and concepts that apply to virtually all public health micronutrient interventions. Countries can adapt it to their context in order to support programme design, implementation, monitoring and evaluation for the successful scale-up of nutrition interventions in public health.
Figures
References
-
- United Nations General Assembly (2000) Resolution 2, Session 55. United Nations Millennium Declaration, 8 September 2000. http://www.un.org/ga/search/view_doc.asp?symbol=A/RES/55/2&Lang=E
-
- United Nations General Assembly (2010) Resolution 1, Session 65. Keeping the promise: united to achieve the Millennium Development Goals, 19 October 2010. http://www.un.org/en/mdg/summit2010/pdf/outcome_documentN1051260.pdf
-
- World Health Organization (2009) Global Health Risks: Mortality and Burden of Disease Attributable to Selected Major Risks. Geneva: WHO; available at http://www.who.int/healthinfo/global_burden_disease/GlobalHealthRisks_re...
-
- Horton S, Shekar M, McDonald C et al. (2010) Scaling Up Nutrition: What will it cost? Washington, DC: World Bank, available at http://siteresources.worldbank.org/HealthNutritionandPopulation/Resource...
-
- Pena-Rosas JP, De-Regil LM, Rogers LM et al. (2012) Translating research into action: WHO evidence-informed guidelines for safe and effective micronutrient interventions. J Nutr 142, issue 1, 197S–204S. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical