A randomized comparison of a commercially available portion-controlled weight-loss intervention with a diabetes self-management education program
- PMID: 23507967
- PMCID: PMC3608893
- DOI: 10.1038/nutd.2013.3
A randomized comparison of a commercially available portion-controlled weight-loss intervention with a diabetes self-management education program
Abstract
Objective: This study examined the efficacy of a commercially available, portion-controlled diet (PCD) on body weight and HbA1c over 6 months in obese patients with type 2 diabetes.
Research design and methods: One-hundred participants with a mean±s.d. age of 55.6±10.6 year, body weight of 102.9±18.4 kg and HbA1c of 7.7±1.3% were randomly assigned to a 9-session group lifestyle intervention that included a PCD or to a 9-session group program of diabetes self-management education (DSME). Participants in the two groups were prescribed the same goals for energy intake (1250-1550 kcal per day) and physical activity (200 min per week).
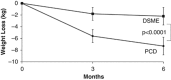
Results: While both groups produced significant improvements in weight and HbA1c after 6 months of treatment, PCD participants lost 7.3 kg [95% confidence interval (CI): -5.8 to -8.8 kg], compared with 2.2 kg (95% CI: -0.7 to -3.7 kg) in the DSME group (P<0.0001). Significantly more PCD than DSME participants lost 5% of initial weight (54.0% vs 14.0%, P<0.0001) and 10% (26.0% vs 6.0%, P<0.0001). HbA1c declined by 0.7% (95% CI: -0.4 to -1.0%) in the PCD group, compared with 0.4% (95% CI: -0.1 to -0.7%) in DSME (P<0.026). Across both groups, larger weight losses were associated with greater reductions in HbA1c (r=0.52, P<0.0001).
Conclusions: These findings demonstrate that a commercially available portion-controlled meal plan can induce clinically meaningful improvements in weight and glycemic control in obese individuals with type 2 diabetes. These data have implications for the management of obesity in primary care, as now provided by the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services.
Figures
References
-
- Tuomilehto J, Lindstrom J, Eriksson JG, Valle TT, Hamalainen H, Ilanne-Parikka P, et al. Prevention of type 2 diabetes mellitus by changes in lifestyle among subjects with impaired glucose tolerance. N Engl J Med. 2001;344:1343–1350. - PubMed
-
- National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute Clinical Guidelines on the Identification, Evaluation, and Treatment of Overweight and Obesity in Adults--The Evidence Report. Obes Res. 1998;6 (Suppl 2:51S–209S. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources