Radioprotective effect of melatonin in reducing oxidative stress in rat lenses
- PMID: 23508093
- PMCID: PMC3584458
Radioprotective effect of melatonin in reducing oxidative stress in rat lenses
Abstract
Objective: Ocular morbidity is widely observed when radiotherapy includes the orbit. Oxidative stress generated by irradiation is responsible for this complication. In different studies, it has been shown that melatonin has antioxidative properties and a radioprotective role. The aim of this study was to evaluate the antioxidant role of melatonin against radiation-induced oxidative injury in rats' lenses after total cranial irradiation.
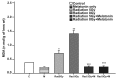
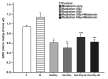
Materials and methods: Thirty-six adult female Sprague-Dawley rats were divided into six groups. Group I was the control group, group II only received total cranial gamma irradiation of 5 Gy, group III was exposed as the second group but at the dose of 8 Gy, group IV received 30 mg/kg melatonin 30 minutes prior to radiation plus total cranial irradiation of 5 Gy plus 5 mg/kg melatonin daily through intraperitoneal injection for ten days after irradiation, group V was treated similar to the fourth group, i.e. received irradiation plus melatonin, but at the dose of 8 Gy, and group VI only received melatonin (30 mg/kg on the first day and 5 mg/kg on the following days). Ten days after irradiation, all rats were sacrificed and their eyes were enucleated to measure the biochemical parameters i.e. malondialdehyde (MDA) and glutathione (GSH).
Results: The levels of MDA in rat lenses increased and the levels of glutathione in lenses decreased after gamma ray irradiation but these parameters were still within normal limits in rats that received melatonin.
Conclusion: It could be concluded that melatonin is useful in preventing radiation-induced oxidative injury due to its antioxidative and free radical scavenging properties.
Keywords: Cataract; Free Radicals; Melatonin; Radiation; Radioprotector.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Evaluation of radio-protective effect of melatonin on whole body irradiation induced liver tissue damage.Cell J. 2013 Winter;14(4):292-7. Epub 2013 Feb 20. Cell J. 2013. PMID: 23577309 Free PMC article.
-
Radioprotective effects of melatonin on radiation-induced cataract.J Radiat Res. 2005 Jun;46(2):277-82. doi: 10.1269/jrr.46.277. J Radiat Res. 2005. PMID: 15988147
-
Melatonin reduces oxidative stress in the rat lens due to radiation-induced oxidative injury.Int J Radiat Biol. 2008 Oct;84(10):803-8. doi: 10.1080/09553000802390932. Int J Radiat Biol. 2008. PMID: 18979314
-
The effect of L-carnitine in the prevention of ionizing radiation-induced cataracts: a rat model.Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2007 Apr;245(4):588-94. doi: 10.1007/s00417-005-0097-1. Epub 2006 Aug 17. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2007. PMID: 16915402
-
Ameliorative effect of melatonin against gamma-irradiation-induced oxidative stress and tissue injury.Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2007 Feb;66(2):278-86. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2006.03.008. Epub 2006 Jun 21. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2007. PMID: 16793135
Cited by
-
Utility of melatonin in mitigating ionizing radiation-induced testis injury through synergistic interdependence of its biological properties.Biol Res. 2022 Nov 4;55(1):33. doi: 10.1186/s40659-022-00401-6. Biol Res. 2022. PMID: 36333811 Free PMC article.
-
Melatonin reduces radiation damage in inner ear.J Radiat Res. 2021 Mar 10;62(2):217-225. doi: 10.1093/jrr/rraa137. J Radiat Res. 2021. PMID: 33454767 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of radio-protective effect of melatonin on whole body irradiation induced liver tissue damage.Cell J. 2013 Winter;14(4):292-7. Epub 2013 Feb 20. Cell J. 2013. PMID: 23577309 Free PMC article.
-
Radio-protective role of antioxidant agents.Oncol Rev. 2012 Oct 2;6(2):e16. doi: 10.4081/oncol.2012.e16. eCollection 2012 Oct 2. Oncol Rev. 2012. PMID: 25992214 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Consequences of lethal-whole-body gamma radiation and possible ameliorative role of melatonin.ScientificWorldJournal. 2014;2014:621570. doi: 10.1155/2014/621570. Epub 2014 Nov 5. ScientificWorldJournal. 2014. PMID: 25431791 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Barabino S, Raghavan A, Loeffler J, Dana R. Radiotherapy-induced ocular surface disease. Cornea. 2005;24(8):909–914. - PubMed
-
- Dynlacht JR, Tyree C, Valluri S, DesRosiers C, Caperell-Grant A, Mendonca MS, et al. Effect of estrogen on radiationinduced cataractogenesis. Radiat Res. 2006;165(1):9–16. - PubMed
-
- Beyzadeoglu M, Dirican B, Oysul K, Arpaci F, Pak Y. Evaluation of fractionated total body irradiation and dose rate on cataractogenesis in bone marrow transplantation. Haematologia (Budap) 2002;32(1):25–30. - PubMed
-
- Frisk P, Hagberg H, Mandahl A, Söderberg P, Lönnerholm G. Cataract in children after autologous bone marrow transplantation. A common, but curable complication. Lakartidningen. 2002;99(13):1444–1447. - PubMed
-
- Van Kempen-Harteveld ML, Belkacémi Y, Kal HB, Labopin M, Frassoni F. Dose-effect relationship for cataract induction after single-dose total body irradiation and bone marrow transplantation for acute leukemia. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2002;52(5):1367–1374. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
