IL-1β inhibits human osteoblast migration
- PMID: 23508571
- PMCID: PMC3646095
- DOI: 10.2119/molmed.2012.00058
IL-1β inhibits human osteoblast migration
Abstract
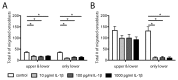
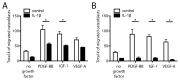
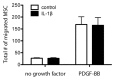
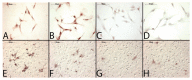
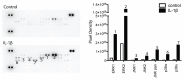
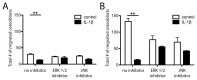
Bone has a high capacity for self-renewal and repair. Prolonged local secretion of interleukin 1β (IL-1β), however, is known to be associated with severe bone loss and delayed fracture healing. Since induction of bone resorption by IL-1β may not sufficiently explain these pathologic processes, we investigated, in vitro, if and how IL-1β affects migration of multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells (MSC) or osteoblasts. We found that homogenous exposure to IL-1β significantly diminished both nondirectional migration and site-directed migration toward the chemotactic factors platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF)-BB and insulin like growth factor 1 (IGF-1) in osteoblasts. Exposure to a concentration gradient of IL-1β induced an even stronger inhibition of migration and completely abolished the migratory response of osteoblasts toward PDGF-BB, IGF-1, vascular endothelial growth factor A (VEGF-A) and the complement factor C5a. IL-1β induced extracellular signal-regulated kinases 1 and 2 (ERK1/2) and c-Jun N-terminal kinases (JNK) activation and inhibition of these signaling pathways suggested an involvement in the IL-1β effects on osteoblast migration. In contrast, basal migration of MSC and their migratory activity toward PDGF-BB was found to be unaffected by IL-1β. These results indicate that the presence of IL-1β leads to impaired recruitment of osteoblasts which might influence early stages of fracture healing and could have pathological relevance for bone remodeling in inflammatory bone disease.
Figures

References
-
- McKibbin B. The biology of fracture healing in long bones. J. Bone Joint Surg. Br. 1978;60-B:150–62. - PubMed
-
- Gerstenfeld LC, Cullinane DM, Barnes GL, Graves DT, Einhorn TA. Fracture healing as a post-natal developmental process: molecular, spatial, and temporal aspects of its regulation. J. Cell. Biochem. 2003;88:873–84. - PubMed
-
- Claes L, Recknagel S, Ignatius A. Fracture healing under healthy and inflammatory conditions. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2012;8:133–43. - PubMed
-
- Lind M, et al. Chemotaxis of human osteoblasts. Effects of osteotropic growth factors. APMIS. 1995;103:140–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

