Cardiac lipotoxicity: molecular pathways and therapeutic implications
- PMID: 23508767
- PMCID: PMC3647019
- DOI: 10.1007/s11897-013-0133-0
Cardiac lipotoxicity: molecular pathways and therapeutic implications
Abstract
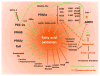
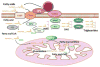
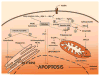
Diabetes and obesity are both associated with lipotoxic cardiomyopathy exclusive of coronary artery disease and hypertension. Lipotoxicities have become a public health concern and are responsible for a significant portion of clinical cardiac disease. These abnormalities may be the result of a toxic metabolic shift to more fatty acid and less glucose oxidation with concomitant accumulation of toxic lipids. Lipids can directly alter cellular structures and activate downstream pathways leading to toxicity. Recent data have implicated fatty acids and fatty acyl coenzyme A, diacylglycerol, and ceramide in cellular lipotoxicity, which may be caused by apoptosis, defective insulin signaling, endoplasmic reticulum stress, activation of protein kinase C, MAPK activation, or modulation of PPARs.
Conflict of interest statement
Konstantinos Drosatos declares that he has no conflict of interest.
P. Christian Schulze declares that he has no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The beneficial impact of curcumin on cardiac lipotoxicity.J Pharm Pharmacol. 2024 Oct 3;76(10):1269-1283. doi: 10.1093/jpp/rgae102. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39180454 Review.
-
Insulin Resistance, Obesity and Lipotoxicity.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017;960:277-304. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-48382-5_12. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017. PMID: 28585204 Review.
-
The role of cardiac lipotoxicity in the pathogenesis of diabetic cardiomyopathy.Expert Rev Cardiovasc Ther. 2014 Mar;12(3):345-58. doi: 10.1586/14779072.2014.891939. Epub 2014 Feb 19. Expert Rev Cardiovasc Ther. 2014. PMID: 24552544 Review.
-
Lipid metabolism and toxicity in the heart.Cell Metab. 2012 Jun 6;15(6):805-12. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2012.04.006. Cell Metab. 2012. PMID: 22682221 Free PMC article.
-
Type 1 diabetic cardiomyopathy in the Akita (Ins2WT/C96Y) mouse model is characterized by lipotoxicity and diastolic dysfunction with preserved systolic function.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2009 Dec;297(6):H2096-108. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00452.2009. Epub 2009 Oct 2. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2009. PMID: 19801494
Cited by
-
Fatty old hearts: role of cardiac lipotoxicity in age-related cardiomyopathy.Pathobiol Aging Age Relat Dis. 2016 Aug 23;6:32221. doi: 10.3402/pba.v6.32221. eCollection 2016. Pathobiol Aging Age Relat Dis. 2016. PMID: 27558317 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Magnolia bioactive constituent 4-O-methylhonokiol prevents the impairment of cardiac insulin signaling and the cardiac pathogenesis in high-fat diet-induced obese mice.Int J Biol Sci. 2015 Jun 5;11(8):879-91. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.12101. eCollection 2015. Int J Biol Sci. 2015. PMID: 26157343 Free PMC article.
-
Canagliflozin and Dapagliflozin Attenuate Glucolipotoxicity-Induced Oxidative Stress and Apoptosis in Cardiomyocytes via Inhibition of Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter-1.ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci. 2022 Mar 9;5(4):216-225. doi: 10.1021/acsptsci.1c00207. eCollection 2022 Apr 8. ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci. 2022. PMID: 35434529 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of l-Carnitine in Mitochondria, Prevention of Metabolic Inflexibility and Disease Initiation.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Feb 28;23(5):2717. doi: 10.3390/ijms23052717. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35269860 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Curcumin‑loaded PEG‑PDLLA nanoparticles for attenuating palmitate‑induced oxidative stress and cardiomyocyte apoptosis through AMPK pathway.Int J Mol Med. 2019 Aug;44(2):672-682. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2019.4228. Epub 2019 Jun 5. Int J Mol Med. 2019. PMID: 31173176 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Augustus AS, Buchanan J, Park TS, Hirata K, Noh HL, Sun J, Homma S, D’Armiento J, Abel ED, Goldberg IJ. Loss of lipoprotein lipase-derived fatty acids leads to increased cardiac glucose metabolism and heart dysfunction. J Biol Chem. 2006;281:8716–8723. - PubMed
-
- Taegtmeyer H, McNulty P, Young ME. Adaptation and maladaptation of the heart in diabetes: Part i: General concepts. Circulation. 2002;105:1727–1733. - PubMed
-
- Stanley WC, Lopaschuk GD, Hall JL, McCormack JG. Regulation of myocardial carbohydrate metabolism under normal and ischaemic conditions. Potential for pharmacological interventions. Cardiovasc Res. 1997;33:243–257. - PubMed
-
- Tamboli A, O’Looney P, Vander Maten M, Vahouny GV. Comparative metabolism of free and esterified fatty acids by the perfused rat heart and rat cardiac myocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983;750:404–410. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

