Antioxidant capacity and the correlation with major phenolic compounds, anthocyanin, and tocopherol content in various extracts from the wild edible Boletus edulis mushroom
- PMID: 23509707
- PMCID: PMC3591155
- DOI: 10.1155/2013/313905
Antioxidant capacity and the correlation with major phenolic compounds, anthocyanin, and tocopherol content in various extracts from the wild edible Boletus edulis mushroom
Abstract
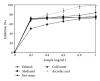
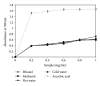
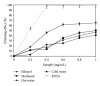
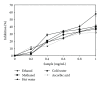
Boletus edulis is a wild edible mushroom habitually consumed by rural populations. Ethanolic and methanolic extracts was obtained in cold and hot water from dried fruit bodies. The antioxidant activity of freeze-dried extracts from B. edulis were investigated using free radicals scavenging activity, reducing power, metal chelating effect, inhibition of lipid peroxidation, and the identification of antioxidant compounds. The levels of different compounds with antioxidant properties were higher in alcoholic extracts compared with aqueous extracts. Rosmarinic acid was the major phenolic compound, it being identified in a concentration between 7 ± 0.23 and 56 ± 0.15 mg/100 g extract. A positive correlation between the content of total phenols, flavonoids, anthocyanins, and tocopherols, and the antioxidant capacity of the extracts was determined. The results showed that the ethanolic extract of Romanian wild mushroom B. edulis represents a natural source of functional compounds.
Figures


References
-
- Rai M, Tidke G, Wasser SP. Therapeutic potential of mushrooms. Natural Product Radiance. 2005;4:246–257.
-
- Elmastas M, Isildak O, Turkekul I, Temur N. Determination of antioxidant activity and antioxidant compounds in wild edible mushrooms. Journal of Food Composition and Analysis. 2007;20(3-4):337–345.
-
- Mattila P, Lampi AM, Ronkainen R, Toivo J, Piironen V. Sterol and vitamin D2 contents in some wild and cultivated mushrooms. Food Chemistry. 2002;76(3):293–298.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

