In vitro antibacterial and antibiofilm activities of chlorogenic acid against clinical isolates of Stenotrophomonas maltophilia including the trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole resistant strain
- PMID: 23509719
- PMCID: PMC3591175
- DOI: 10.1155/2013/392058
In vitro antibacterial and antibiofilm activities of chlorogenic acid against clinical isolates of Stenotrophomonas maltophilia including the trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole resistant strain
Abstract
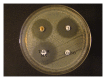
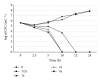
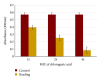
The in vitro antibacterial and antibiofilm activity of chlorogenic acid against clinical isolates of Stenotrophomonas maltophilia was investigated through disk diffusion, minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC), minimum bactericidal concentration (MBC), time-kill and biofilm assays. A total of 9 clinical S. maltophilia isolates including one isolate resistant to trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole (TMP/SMX) were tested. The inhibition zone sizes for the isolates ranged from 17 to 29 mm, while the MIC and MBC values ranged from 8 to 16 μg mL(-1) and 16 to 32 μg mL(-1). Chlorogenic acid appeared to be strongly bactericidal at 4x MIC, with a 2-log reduction in viable bacteria at 10 h. In vitro antibiofilm testing showed a 4-fold reduction in biofilm viability at 4x MIC compared to 1x MIC values (0.085 < 0.397 A 490 nm) of chlorogenic acid. The data from this study support the notion that the chlorogenic acid has promising in vitro antibacterial and antibiofilm activities against S. maltophilia.
Figures
References
-
- Falagas ME, Valkimadi PE, Huang YT, Matthaiou DK, Hsueh PR. Therapeutic options for Stenotrophomonas maltophilia infections beyond co-trimoxazole: a systematic review. Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy. 2008;62(5):889–894. - PubMed
-
- Bywater RJ, Casewell MW. An assessment of the impact of antibiotic resistance in different bacterial species and of the contribution of animal sources to resistance in human infections. Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy. 2000;46(4):643–645. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

