Biochemical characterization and pharmacological properties of new basic PLA2 BrTX-I isolated from Bothrops roedingeri (Roedinger's Lancehead) Mertens, 1942, snake venom
- PMID: 23509747
- PMCID: PMC3591238
- DOI: 10.1155/2013/591470
Biochemical characterization and pharmacological properties of new basic PLA2 BrTX-I isolated from Bothrops roedingeri (Roedinger's Lancehead) Mertens, 1942, snake venom
Abstract
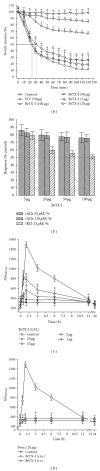
BrTX-I, a PLA2, was purified from Bothrops roedingeri venom after only one chromatographic step using reverse-phase HPLC on μ-Bondapak C-18 column. A molecular mass of 14358.69 Da was determined by MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry. Amino acid analysis showed a high content of hydrophobic and basic amino acids as well as 14 half-cysteine residues. The total amino acid sequence was obtained using SwissProt database and showed high amino acid sequence identity with other PLA2 from snake venom. The amino acid composition showed that BrTX-I has a high content of Lys, Tyr, Gly, Pro, and 14 half-Cys residues, typical of a basic PLA2. BrTX-I presented PLA2 activity and showed a minimum sigmoidal behavior, reaching its maximal activity at pH 8.0, 35-45°C, and required Ca(2+). In vitro, the whole venom and BrTX-I caused a neuromuscular blockade in biventer cervicis preparations in a similar way to other Bothrops species. BrTX-I induced myonecrosis and oedema-forming activity analyzed through injection of the purified BrTX-I in mice. Since BrTX-I exerts a strong proinflammatory effect, the enzymatic phospholipid hydrolysis might be relevant for these phenomena; incrementing levels of IL-1, IL-6, and TNF α were observed at 15 min, 30 min, one, two, and six hours postinjection, respectively.
Figures





References
-
- Kini RM. Excitement ahead: structure, function and mechanism of snake venom phospholipase A2 enzymes. Toxicon. 2003;42(8):827–840. - PubMed
-
- Majunatha Kini R, Evans HJ. A model to explain the pharmacological effects of snake venom phospholipases A2 . Toxicon. 1989;27(6):613–635. - PubMed
-
- Gutiérrez JM, Ownby CL. Skeletal muscle degeneration induced by venom phospholipases A2: insights into the mechanisms of local and systemic myotoxicity. Toxicon. 2003;42(8):915–931. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

