Genome-wide association and regional heritability mapping to identify loci underlying variation in nematode resistance and body weight in Scottish Blackface lambs
- PMID: 23512009
- PMCID: PMC3630823
- DOI: 10.1038/hdy.2012.90
Genome-wide association and regional heritability mapping to identify loci underlying variation in nematode resistance and body weight in Scottish Blackface lambs
Abstract
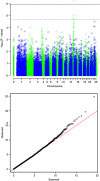
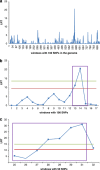
The genetic architecture underlying nematode resistance and body weight in Blackface lambs was evaluated comparing genome-wide association (GWA) and regional heritability mapping (RHM) approaches. The traits analysed were faecal egg count (FEC) and immunoglobulin A activity against third-stage larvae from Teladorsagia circumcincta, as indicators of nematode resistance, and body weight in a population of 752 Scottish Blackface lambs, genotyped with the 50k single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) chip. FEC for both Nematodirus and Strongyles nematodes (excluding Nematodirus), as well as body weight were collected at approximately 16, 20 and 24 weeks of age. In addition, a weighted average animal effect was estimated for both FEC and body weight traits. After quality control, 44 388 SNPs were available for the GWA analysis and 42 841 for the RHM, which utilises only mapped SNPs. The same fixed effects were used in both analyses: sex, year, management group, litter size and age of dam, with day of birth as covariate. Some genomic regions of interest for both nematode resistance and body weight traits were identified, using both GWA and RHM approaches. For both methods, strong evidence for association was found on chromosome 14 for Nematodirus average animal effect, chromosome 6 for Strongyles FEC at 16 weeks and chromosome 6 for body weight at 16 weeks. Across the entire data set, RHM identified more regions reaching the suggestive level than GWA, suggesting that RHM is capable of capturing some of the variation not detected by GWA analyses.
Figures


Similar articles
-
A joint analysis to identify loci underlying variation in nematode resistance in three European sheep populations.J Anim Breed Genet. 2014 Dec;131(6):426-36. doi: 10.1111/jbg.12071. Epub 2014 Jan 8. J Anim Breed Genet. 2014. PMID: 24397290 Free PMC article.
-
An independent validation study of loci associated with nematode resistance in sheep.Anim Genet. 2018 Jun;49(3):265-268. doi: 10.1111/age.12649. Epub 2018 Mar 23. Anim Genet. 2018. PMID: 29570808
-
Genome-wide association studies of parasite resistance, productivity and immunology traits in Scottish Blackface sheep.Animal. 2024 Feb;18(2):101069. doi: 10.1016/j.animal.2023.101069. Epub 2024 Jan 22. Animal. 2024. PMID: 38296768
-
How lambs control infection with Ostertagia circumcincta.Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 1999 Dec 15;72(1-2):213-8. doi: 10.1016/s0165-2427(99)00134-8. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 1999. PMID: 10614511 Review.
-
Targeted flock/herd and individual ruminant treatment approaches.Vet Parasitol. 2012 May 4;186(1-2):10-7. doi: 10.1016/j.vetpar.2011.11.041. Epub 2011 Nov 20. Vet Parasitol. 2012. PMID: 22188982 Review.
Cited by
-
Genotyping of major histocompatibility complex Class II DRB gene in Rohilkhandi goats by polymerase chain reaction-restriction fragment length polymorphism and DNA sequencing.Vet World. 2015 Oct;8(10):1183-8. doi: 10.14202/vetworld.2015.1183-1188. Epub 2015 Oct 9. Vet World. 2015. PMID: 27047015 Free PMC article.
-
Single Nucleotide Polymorphism Effects on Lamb Fecal Egg Count Estimated Breeding Values in Progeny-Tested Katahdin Sires.Front Genet. 2022 May 3;13:866176. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.866176. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 35591856 Free PMC article.
-
Unveiling genomic regions that underlie differences between Afec-Assaf sheep and its parental Awassi breed.Genet Sel Evol. 2017 Feb 10;49(1):19. doi: 10.1186/s12711-017-0296-3. Genet Sel Evol. 2017. PMID: 28187715 Free PMC article.
-
A joint analysis to identify loci underlying variation in nematode resistance in three European sheep populations.J Anim Breed Genet. 2014 Dec;131(6):426-36. doi: 10.1111/jbg.12071. Epub 2014 Jan 8. J Anim Breed Genet. 2014. PMID: 24397290 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide association study and genomic heritabilities for blood protein levels in Lori-Bakhtiari sheep.Sci Rep. 2021 Dec 9;11(1):23771. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-03290-z. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34887490 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aulchenko YS, Ripke S, Isaacs A, van Duijn CM. GenABEL: an R library for genome-wide association analysis. Bioinformatics. 2007;23:1294–1296. - PubMed
-
- Bairden K.1991Ruminant parasitic gastroenteritis: some observations on epidemiology and controlPhD Thesis, University of Glasgow.
-
- Bartley DJ, Jackson F, Jackson E, Sargison N. Characterization of two triple resistant field isolates of Teladorsagia from Scottish lowland sheep farms. Vet Parasitol. 2004;123:189–199. - PubMed
-
- Beh KJ, Hulme DJ, Callaghan MJ, Leish Z, Lenane I, Windon RG, et al. A genome scan for quantitative trait loci affecting resistance to Trichostrongylus colubriformis in sheep. Anim Genet. 2002;93:97–106. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

