Interplay among RNA polymerases II, IV and V in RNA-directed DNA methylation at a low copy transgene locus in Arabidopsis thaliana
- PMID: 23512103
- PMCID: PMC3646161
- DOI: 10.1007/s11103-013-0041-4
Interplay among RNA polymerases II, IV and V in RNA-directed DNA methylation at a low copy transgene locus in Arabidopsis thaliana
Abstract
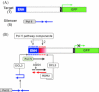
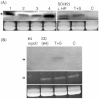
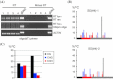
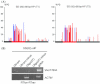
RNA-directed DNA methylation (RdDM) is an epigenetic process whereby small interfering RNAs (siRNAs) guide cytosine methylation of homologous DNA sequences. RdDM requires two specialized RNA polymerases: Pol IV transcribes the siRNA precursor whereas Pol V generates scaffold RNAs that interact with siRNAs and attract the methylation machinery. Recent evidence also suggests the involvement of RNA polymerase II (Pol II) in recruiting Pol IV and Pol V to low copy, intergenic loci. We demonstrated previously that Pol V-mediated methylation at a transgene locus in Arabidopsis spreads downstream of the originally targeted region by means of Pol IV/RNA-DEPENDENT RNA POLYMERASE2 (RDR2)-dependent 24-nt secondary siRNAs. Here we show that these secondary siRNAs can not only induce methylation in cis but also in trans at an unlinked target site, provided this sequence is transcribed by Pol II to produce a non-coding RNA. The Pol II transcript appears to be important for amplification of siRNAs at the unlinked target site because its presence correlates not only with methylation but also with elevated levels of 24-nt siRNAs. Potential target sites that lack an overlapping Pol II transcript and remain unmethylated in the presence of trans-acting 24-nt siRNAs can nevertheless acquire methylation in the presence of 21-24-nt hairpin-derived siRNAs, suggesting that RdDM of non-transcribed target sequences requires multiple size classes of siRNA. Our findings demonstrate that Pol II transcripts are not always needed for RdDM at low copy loci but they may intensify RdDM by facilitating amplification of Pol IV-dependent siRNAs at the DNA target site.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Distinct and concurrent pathways of Pol II- and Pol IV-dependent siRNA biogenesis at a repetitive trans-silencer locus in Arabidopsis thaliana.Plant J. 2014 Jul;79(1):127-38. doi: 10.1111/tpj.12545. Epub 2014 Jun 13. Plant J. 2014. PMID: 24798377
-
RNA polymerases IV and V influence the 3' boundaries of Polymerase II transcription units in Arabidopsis.RNA Biol. 2018 Feb 1;15(2):269-279. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2017.1409930. Epub 2017 Dec 21. RNA Biol. 2018. PMID: 29199514 Free PMC article.
-
NRPD4, a protein related to the RPB4 subunit of RNA polymerase II, is a component of RNA polymerases IV and V and is required for RNA-directed DNA methylation.Genes Dev. 2009 Feb 1;23(3):318-30. doi: 10.1101/gad.1765209. Genes Dev. 2009. PMID: 19204117 Free PMC article.
-
RNA-directed DNA methylation in plants: Where to start?RNA Biol. 2013 Oct;10(10):1593-6. doi: 10.4161/rna.26312. RNA Biol. 2013. PMID: 25003825 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The RNAs of RNA-directed DNA methylation.Biochim Biophys Acta Gene Regul Mech. 2017 Jan;1860(1):140-148. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2016.08.004. Epub 2016 Aug 10. Biochim Biophys Acta Gene Regul Mech. 2017. PMID: 27521981 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The ability to form homodimers is essential for RDM1 to function in RNA-directed DNA methylation.PLoS One. 2014 Feb 3;9(2):e88190. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0088190. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24498436 Free PMC article.
-
Maize RNA PolIV affects the expression of genes with nearby TE insertions and has a genome-wide repressive impact on transcription.BMC Plant Biol. 2017 Oct 12;17(1):161. doi: 10.1186/s12870-017-1108-1. BMC Plant Biol. 2017. PMID: 29025411 Free PMC article.
-
Reconstructing de novo silencing of an active plant retrotransposon.Nat Genet. 2013 Sep;45(9):1029-39. doi: 10.1038/ng.2703. Epub 2013 Jul 14. Nat Genet. 2013. PMID: 23852169
-
Targeting Argonaute to chromatin.Genes Dev. 2016 Dec 15;30(24):2649-2650. doi: 10.1101/gad.294900.116. Genes Dev. 2016. PMID: 28087710 Free PMC article.
-
Small RNAs: essential regulators of gene expression and defenses against environmental stresses in plants.Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2016 May;7(3):356-81. doi: 10.1002/wrna.1340. Epub 2016 Feb 28. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2016. PMID: 26924473 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

