Normalization of mass cytometry data with bead standards
- PMID: 23512433
- PMCID: PMC3688049
- DOI: 10.1002/cyto.a.22271
Normalization of mass cytometry data with bead standards
Abstract
Mass cytometry uses atomic mass spectrometry combined with isotopically pure reporter elements to currently measure as many as 40 parameters per single cell. As with any quantitative technology, there is a fundamental need for quality assurance and normalization protocols. In the case of mass cytometry, the signal variation over time due to changes in instrument performance combined with intervals between scheduled maintenance must be accounted for and then normalized. Here, samples were mixed with polystyrene beads embedded with metal lanthanides, allowing monitoring of mass cytometry instrument performance over multiple days of data acquisition. The protocol described here includes simultaneous measurements of beads and cells on the mass cytometer, subsequent extraction of the bead-based signature, and the application of an algorithm enabling correction of both short- and long-term signal fluctuations. The variation in the intensity of the beads that remains after normalization may also be used to determine data quality. Application of the algorithm to a one-month longitudinal analysis of a human peripheral blood sample reduced the range of median signal fluctuation from 4.9-fold to 1.3-fold.
Copyright © 2013 International Society for Advancement of Cytometry.
Figures
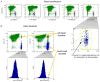



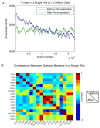

Comment in
-
Another step on the path to mass cytometry standardization.Cytometry A. 2015 May;87(5):380-2. doi: 10.1002/cyto.a.22661. Epub 2015 Apr 9. Cytometry A. 2015. PMID: 25904393 No abstract available.
References
-
- Bandura DR, et al. Mass Cytometry: Technique for Real Time Single Cell Multitarget Immunoassay Based on Inductively Coupled Plasma Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry. Anal Chem. 2009 - PubMed
-
- Perfetto SP, et al. Quality assurance for polychromatic flow cytometry. Nature protocols. 2006;1(3):1522–30. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 CA130826/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- RFA CA 09-009/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- PN2 EY018228/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA034233/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AI057229/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- 1R01CA130826/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U54 CA149145/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA034233-22A1/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 0158 G KB065/PHS HHS/United States
- U54 CA119367/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN272200700038C/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- RFA CA 09-011/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- PN2EY018228/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

