Chemical probes of endocannabinoid metabolism
- PMID: 23512546
- PMCID: PMC3639726
- DOI: 10.1124/pr.112.006387
Chemical probes of endocannabinoid metabolism
Abstract
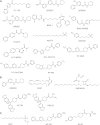
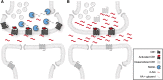
The endocannabinoid signaling system regulates diverse physiologic processes and has attracted considerable attention as a potential pharmaceutical target for treating diseases, such as pain, anxiety/depression, and metabolic disorders. The principal ligands of the endocannabinoid system are the lipid transmitters N-arachidonoylethanolamine (anandamide) and 2-arachidonoylglycerol (2-AG), which activate the two major cannabinoid receptors, CB1 and CB2. Anandamide and 2-AG signaling pathways in the nervous system are terminated by enzymatic hydrolysis mediated primarily by the serine hydrolases fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH) and monoacylglycerol lipase (MAGL), respectively. In this review, we will discuss the development of FAAH and MAGL inhibitors and their pharmacological application to investigate the function of anandamide and 2-AG signaling pathways in preclinical models of neurobehavioral processes, such as pain, anxiety, and addiction. We will place emphasis on how these studies are beginning to discern the different roles played by anandamide and 2-AG in the nervous system and the resulting implications for advancing endocannabinoid hydrolase inhibitors as next-generation therapeutics.
Figures





References
-
- Abouabdellah A, Almario GA, Hoornaert C, Lardenois P, Marguet F. (2005) inventors; Sanofi-Aventis, assignee. Aryl- and heteroaryl-piperidinecarboxylate derivatives, their preparation and use as fatty acid amido hydrolase (FAAH) inhibitors for treating FAAH-related pathologies. World Patent WO 2005/090347. 2005 Sep 29.
-
- Ahn K, Johnson DS, Fitzgerald LR, Liimatta M, Arendse A, Stevenson T, Lund ET, Nugent RA, Nomanbhoy TK, Alexander JP, et al. (2007) Novel mechanistic class of fatty acid amide hydrolase inhibitors with remarkable selectivity. Biochemistry 46:13019–13030 - PubMed
-
- Ahn K, Smith SE, Liimatta MB, Beidler D, Sadagopan N, Dudley DT, Young T, Wren P, Zhang Y, Swaney S, et al. (2011) Mechanistic and pharmacological characterization of PF-04457845: a highly potent and selective fatty acid amide hydrolase inhibitor that reduces inflammatory and noninflammatory pain. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 338:114–124 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

