Human xenografts are not rejected in a naturally occurring immunodeficient porcine line: a human tumor model in pigs
- PMID: 23514746
- PMCID: PMC3559234
- DOI: 10.1089/biores.2012.9902
Human xenografts are not rejected in a naturally occurring immunodeficient porcine line: a human tumor model in pigs
Abstract
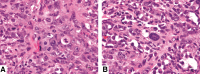
Animal models for cancer therapy are invaluable for preclinical testing of potential cancer treatments; however, therapies tested in such models often fail to translate into clinical settings. Therefore, a better preclinical model for cancer treatment testing is needed. Here we demonstrate that an immunodeficient line of pigs can host and support the growth of xenografted human tumors and has the potential to be an effective animal model for cancer therapy. Wild-type and immunodeficient pigs were injected subcutaneously in the left ear with human melanoma cells (A375SM cells) and in the right ear with human pancreatic carcinoma cells (PANC-1). All immunodeficient pigs developed tumors that were verified by histology and immunohistochemistry. Nonaffected littermates did not develop tumors. Immunodeficient pigs, which do not reject xenografted human tumors, have the potential to become an extremely useful animal model for cancer therapy because of their similarity in size, anatomy, and physiology to humans.
Keywords: immunodeficient swine; large-animal cancer model; melanoma; pancreatic carcinoma; xenografts.
Figures




References
-
- Rothenberg ML. Carbone DP. Johnson DH. Improving the evaluation of new cancer treatments: challenges and opportunities. Nat Rev Cancer. 2003;3:303–309. - PubMed
-
- Kelland LR. “Of mice and men”: values and liabilities of the athymic nude mouse model in anticancer drug development. Eur J Cancer. 2004;40:827–836. - PubMed
-
- Liu M. Hicklin D. Human tumor xenograft efficacy models. In: Teicher BA, editor. Tumor Models in Cancer Research. Springer; New York: 2010. pp. 99–124.
-
- Sausville EA. Burger AM. Contributions of human tumor xenografts to anticancer drug development. Cancer Res. 2006;66:3351–3354. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
