Comparative efficacy of two leading candidate ricin toxin a subunit vaccines in mice
- PMID: 23515013
- PMCID: PMC3675979
- DOI: 10.1128/CVI.00098-13
Comparative efficacy of two leading candidate ricin toxin a subunit vaccines in mice
Abstract
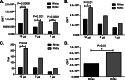
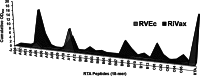
The two leading ricin toxin vaccine candidates, RVEc and RiVax, are recombinant derivatives of the toxin's 267-amino-acid enzymatic A chain (RTA). RVEc is truncated at the C terminus (residues 199 to 267) to improve protein thermostability, while RiVax has two point mutations (V76M and Y80A) that eliminate the RNA N-glycosidase activity of RTA, as well as its ability to induce vascular leak syndrome. The two vaccines have never been directly compared in terms of their ability to stimulate RTA-specific antibodies (Abs), toxin-neutralizing activity (TNA), or protective immunity. To address this issue, groups of female BALB/c mice were immunized two or three times with Alhydrogel-adsorbed RiVax or RVEc at a range of doses (0.3 to 20 μg) and then challenged with 10 50% lethal doses (LD(50)s) of ricin. We found that the vaccines were equally effective at eliciting protective immunity at the doses tested. There were, however, quantitative differences in the antibody responses. RVEc tended to elicit higher levels of ricin-specific RTA IgG and TNA than did RiVax. Pepscan analysis revealed that serum Abs elicited by RVEc were skewed toward a solvent-exposed immunodominant α-helix known to be the target of potent toxin-neutralizing Abs. Finally, immunodepletion experiments suggest that the majority of toxin-neutralizing Abs elicited by RiVax were confined to residues 1 to 198, possibly explaining the equal effectiveness of RVEc as a vaccine.
Figures

References
-
- Endo Y, Tsurugi K. 1987. RNA N-glycosidase activity of ricin A-chain. Mechanism of action of the toxic lectin ricin on eukaryotic ribosomes. J. Biol. Chem. 262:8128–8130 - PubMed
-
- Rutenber E, Ready M, Robertus JD. 1987. Structure and evolution of ricin B chain. Nature 326:624–626 - PubMed
-
- Franz D, Jaax N. 1997. Ricin toxin, p 631–642 In Zajtchuk R. (ed), Textbook of military medicine. Borden Institute, Washington, DC
-
- Radosavljevic V, Belojevic G. 2009. A new model of bioterrorism risk assessment. Biosecur. Bioterror. 7:443–451 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

