Research on the regulation of the spatial structure of acetylcholinesterase tetramer with high efficiency by AFM
- PMID: 23515568
- PMCID: PMC3600998
- DOI: 10.2147/IJN.S41591
Research on the regulation of the spatial structure of acetylcholinesterase tetramer with high efficiency by AFM
Abstract
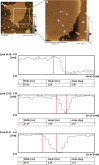
Atomic force microscopy (AFM) was applied for obtaining structural information about acetylcholinesterase (AChE) tetramer (AChE G(4)) before and after reaction with S-acetylcholine iodide (S-ACh), in the presence or absence of propidium iodide (PI), an inhibitor for peripheral anionic sites (PAS). An iced-bath ultrasound was used to prepare the phospholipid membrane. Ves-fusion technique was applied for incorporating AChE G(4) in a lipid layer on mica. Before reaction with substrates, the single AChE G(4) particle was ellipsoid in shape with a clear border. It had a smooth surface with a central projection. The four subunits of a single enzyme particle were arranged tightly (no separated subunits being found, with an average size of 89 ± 7 nm in length, 68 ± 9 nm in width, and 6 ± 3 nm in height). After reaction with S-ACh in the absence of PI, the loose arrangement of subunits of AChE G(4) was seen, with an average size of 104 ± 7 nm in length, 91 ± 5 nm in width, and 8 ± 2 nm in height. Also there was free-flowing space amongst the four subunits of the AChE G(4). This was consistent with the results of the ×-ray diffraction crystallography and molecular dynamics studies. The apparent free space was the central path of AChE G(4), changing from small to big, to small, to lateral door appearance, with an average size of 60 ± 5 nm in length and 51 ± 9 nm in width. The size of lateral door was 52 ± 5 nm in width and 32 ± 3 nm in depth on average. In the presence of PI, S-ACh could not cause topological structure changes of AChE G(4). AFM verified that the central path might govern the turnover of the enzyme morphologically, and the interactions between PI and S-ACh might gate the creation of a central path and the opening of ACG in monomer; and the combination of S-ACh with peripheral anionic sites is conducive to the opening of ACG while PI can inhibit this action. Resolution at the inframolecular level is favorable in providing substantial information on how the spatial structure is adapted to the high efficiency of AChE molecules.
Keywords: ACG; AChE; AFM; Ves-fusion; phospholipid membrane.
Figures



References
-
- Rosenberry TL. Acetylcholinesterase. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1975;43:103–218. - PubMed
-
- Silman I, Sussman JL. Acetylcholinesterase: ‘classical’ and ‘nonclassical’ functions and pharmacology. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2005;5(3):293–302. - PubMed
-
- Sussman JL, Harel M, Frolow F, et al. Atomic structure of acetylcholinesterase from Torpedo californica: a prototypic acetylcholine-binding protein. Science. 1991;253(5022):872–879. - PubMed
-
- Mallender WD, Szegletes T, Rosenberry TL. Acetylthiocholine binds to asp74 at the peripheral site of human acetylcholinesterase as the first step in the catalytic pathway. Biochemistry. 2000;39(26):7753–7763. - PubMed
-
- Johnson JL, Cusack B, Hughes TF, et al. Inhibitors tethered near the acetylcholinesterase active site serve as molecular rulers of the peripheral and acylation sites. J Biol Chem. 2003;278(40):38948–38955. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

