External phenome analysis enables a rational federated query strategy to detect changing rates of treatment-related complications associated with multiple myeloma
- PMID: 23515788
- PMCID: PMC3721159
- DOI: 10.1136/amiajnl-2012-001355
External phenome analysis enables a rational federated query strategy to detect changing rates of treatment-related complications associated with multiple myeloma
Abstract
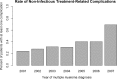
Electronic health records (EHRs) are increasingly useful for health services research. For relatively uncommon conditions, such as multiple myeloma (MM) and its treatment-related complications, a combination of multiple EHR sources is essential for such research. The Shared Health Research Information Network (SHRINE) enables queries for aggregate results across participating institutions. Development of a rational search strategy in SHRINE may be augmented through analysis of pre-existing databases. We developed a SHRINE query for likely non-infectious treatment-related complications of MM, based upon an analysis of the Multiparameter Intelligent Monitoring in Intensive Care (MIMIC II) database. Using this query strategy, we found that the rate of likely treatment-related complications significantly increased from 2001 to 2007, by an average of 6% a year (p=0.01), across the participating SHRINE institutions. This finding is in keeping with increasingly aggressive strategies in the treatment of MM. This proof of concept demonstrates that a staged approach to federated queries, using external EHR data, can yield potentially clinically meaningful results.
Figures
References
-
- Houle D, Govindaraju DR, Omholt S. Phenomics: the next challenge. Nat Rev Genet 2010;11:855–66 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical