Blood-informative transcripts define nine common axes of peripheral blood gene expression
- PMID: 23516379
- PMCID: PMC3597511
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1003362
Blood-informative transcripts define nine common axes of peripheral blood gene expression
Abstract
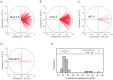
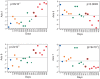
We describe a novel approach to capturing the covariance structure of peripheral blood gene expression that relies on the identification of highly conserved Axes of variation. Starting with a comparison of microarray transcriptome profiles for a new dataset of 189 healthy adult participants in the Emory-Georgia Tech Center for Health Discovery and Well-Being (CHDWB) cohort, with a previously published study of 208 adult Moroccans, we identify nine Axes each with between 99 and 1,028 strongly co-regulated transcripts in common. Each axis is enriched for gene ontology categories related to sub-classes of blood and immune function, including T-cell and B-cell physiology and innate, adaptive, and anti-viral responses. Conservation of the Axes is demonstrated in each of five additional population-based gene expression profiling studies, one of which is robustly associated with Body Mass Index in the CHDWB as well as Finnish and Australian cohorts. Furthermore, ten tightly co-regulated genes can be used to define each Axis as "Blood Informative Transcripts" (BITs), generating scores that define an individual with respect to the represented immune activity and blood physiology. We show that environmental factors, including lifestyle differences in Morocco and infection leading to active or latent tuberculosis, significantly impact specific axes, but that there is also significant heritability for the Axis scores. In the context of personalized medicine, reanalysis of the longitudinal profile of one individual during and after infection with two respiratory viruses demonstrates that specific axes also characterize clinical incidents. This mode of analysis suggests the view that, rather than unique subsets of genes marking each class of disease, differential expression reflects movement along the major normal Axes in response to environmental and genetic stimuli.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures




References
-
- Weedon MN, et al. (2006) Combining information from common type 2 diabetes risk polymorphisms improves disease prediction. PLoS Med 3: e374 doi:10.1371/journal.pmed.0030374 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hamburg MA, Collins FS (2010) The path to personalized medicine. N Engl J Med 363: 301–304. - PubMed
-
- Hood L, Heath JR, Phelps ME, Lin B (2004) Systems biology and new technologies enable predictive and preventative medicine. Science 306: 640–643. - PubMed
-
- Pastinen T (2010) Genome-wide allele-specific analysis: insights into regulatory variation. Nat Rev Genet 11: 533–538. - PubMed
-
- Skelly DA, Ronald J, Akey JM (2009) Inherited variation in gene expression. Annu Rev Genomics Hum Genet 10: 313–332. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

