NT-proBNP, C-reactive protein and soluble uPAR in a bi-ethnic male population: the SAfrEIC study
- PMID: 23516493
- PMCID: PMC3596271
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0058506
NT-proBNP, C-reactive protein and soluble uPAR in a bi-ethnic male population: the SAfrEIC study
Abstract
Objective and design: This cross-sectional study aimed to investigate associations between a marker of cardiac strain, the N-terminal prohormone B-type natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP), and inflammation as reflected by either a conventional or novel inflammatory marker in a bi-ethnic South African cohort.
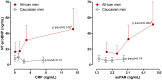
Methods and subjects: We measured NT-proBNP, C-reactive protein (CRP) and plasma-soluble urokinase plasminogen activator receptor (suPAR) levels along with conventional biomarkers in black (n = 117) and white (n = 116) men.
Results: NT-proBNP, CRP and suPAR levels were higher in black compared to white men. NT-proBNP was significantly associated with both CRP (r = 0.38; p = 0.001) and suPAR (r = 0.42; p<0.001) in black men only. After full adjustment in multiple regression analyses, the above associations of NT-proBNP with CRP (β = 0.199; p = 0.018) and suPAR (β = 0.257; p<0.01) were confirmed in black men.
Conclusion: These results suggest that a low-grade inflammatory state as reflected by both a conventional and novel marker of inflammation may contribute to higher cardiovascular risk as reflected by the associations obtained with a marker of cardiac strain in black South African men.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Kengne AP, Anderson CS (2006) The neglected burden of stroke in Sub-Saharan Africa. Int J Stroke 1 4: 180–190. - PubMed
-
- Fourie CMT, Van Rooyen JM, Kruger A, Olsen MH, Eugen-Olsen J, et al. (2012) Soluble urokinase plasminogen activator receptor (suPAR) is associated with metabolic changes in HIV-1-infected Africans: a prospective study. Inflammation 35 1: 221–229. - PubMed
-
- Gottdiener JS, Arnold AM, Aurigemma GP, Polak JF, Tracy RP, et al. (2000) Predictors of congestive heart failure in the elderly: the Cardiovascular Health Study. J Am Coll Cardiol 35: 1628–1637. - PubMed
-
- Yu H, Rifai N (2000) High-sensitivity C-reactive protein and atherosclerosis: from theory to therapy. Clin Biochem 33: 601–610. - PubMed
-
- Ridker PM, Stampfer MJ, Rifai N (2001) Novel risk factors for systemic atherosclerosis. JAMA 285: 2481–2485. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous