Opportunistic visitors: long-term behavioural response of bull sharks to food provisioning in Fiji
- PMID: 23516496
- PMCID: PMC3596312
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0058522
Opportunistic visitors: long-term behavioural response of bull sharks to food provisioning in Fiji
Abstract
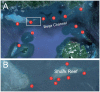
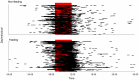
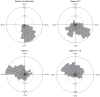
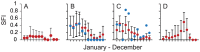
Shark-based tourism that uses bait to reliably attract certain species to specific sites so that divers can view them is a growing industry globally, but remains a controversial issue. We evaluate multi-year (2004-2011) underwater visual (n = 48 individuals) and acoustic tracking data (n = 82 transmitters; array of up to 16 receivers) of bull sharks Carcharhinus leucas from a long-term shark feeding site at the Shark Reef Marine Reserve and reefs along the Beqa Channel on the southern coast of Viti Levu, Fiji. Individual C. leucas showed varying degrees of site fidelity. Determined from acoustic tagging, the majority of C. leucas had site fidelity indexes >0.5 for the marine reserve (including the feeding site) and neighbouring reefs. However, during the time of the day (09:00-12:00) when feeding takes place, sharks mainly had site fidelity indexes <0.5 for the feeding site, regardless of feeding or non-feeding days. Site fidelity indexes determined by direct diver observation of sharks at the feeding site were lower compared to such values determined by acoustic tagging. The overall pattern for C. leucas is that, if present in the area, they are attracted to the feeding site regardless of whether feeding or non-feeding days, but they remain for longer periods of time (consecutive hours) on feeding days. The overall diel patterns in movement are for C. leucas to use the area around the feeding site in the morning before spreading out over Shark Reef throughout the day and dispersing over the entire array at night. Both focal observation and acoustic monitoring show that C. leucas intermittently leave the area for a few consecutive days throughout the year, and for longer time periods (weeks to months) at the end of the calendar year before returning to the feeding site.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures





References
-
- Knight J (2009) Making wildlife viewable: habituation and attraction. Soc Anim 17: 167–184.
-
- Orams MB (2002) Feeding wildlife as a tourism attraction: a review of issues and impacts. Tourism Manage 23: 281–293.
-
- Dobson J (2008) Shark! A new frontier in tourist demand for marine wildlife. In Higham J, Lück M, editors. Marine Wildlife and Tourism Management. Cambridge: CAB International. pp. 49–65.
-
- Brunnschweiler JM (2010) The Shark Reef Marine Reserve: a marine tourism project in Fiji involving local communities. J Sustain Tour 18: 29–42.
-
- Gallagher AJ, Hammerschlag N (2011) Global shark currency: the distribution, frequency, and economic value of shark ecotourism. Curr Issues Tourism 14: 797–812.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

