MiR-181a regulates inflammation responses in monocytes and macrophages
- PMID: 23516523
- PMCID: PMC3596280
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0058639
MiR-181a regulates inflammation responses in monocytes and macrophages
Abstract
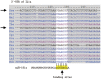
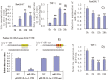
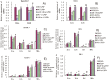
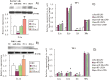
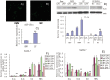
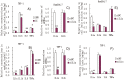
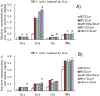
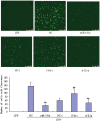
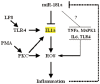
miR-181a has been presumed to target the 3'-untranslated regions (3'-UTR) of IL1a based on software predictions. miR-181a and IL1a have opposite expression levels in monocytes and macrophages in the inflammatory state. This led us to suspect that mir-181a has an important function in regulating inflammatory response by targeting IL1a. Fluorescence reporter assays showed that miR-181a effectively binds to the 3'-UTR of IL1a. The anti-inflammatory functions of miR-181a were investigated in lipopolysaccharides (LPS)-induced Raw264.7 and phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA)/LPS-induced THP-1 cells. We found that miR-181a mimics significantly lowered IL1a expression levels in these cells and, interestingly, miR-181a inhibitors reversed this decrease. In addition, miR-181a mimics significantly inhibited increase in the levels of inflammatory factors (IL1b, IL6, and TNFa) in these cells. Furthermore, miR-181a mimics and inhibitors decreased and increased, respectively, production of reactive oxygen species in PMA/LPS-induced THP-1 cells. These results indicate that miR-181a regulates inflammatory responses by directly targeting the 3'-UTR of IL1a and down-regulating IL1a levels. Interestingly, we found that miR-181a inhibited production of inflammatory factors even in IL1a-induced THP-1 cells, suggesting that the anti-inflammatory effects of miR-181a possibly involves other targets in addition to IL1a. Thus, we provide the first evidence for anti-inflammatory effects of miR-181a mediated at least in part by down-regulating IL1a.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Xie W, Du L (2011) Diabetes is an inflammatory disease: evidences from traditional Chinese Medicines. Diabetes Obes Metab 13: 289–301. - PubMed
-
- Taube A, Schlich R, Sell H, Eckardt K, Eckel J (2012) Inflammation and metabolic dysfunction: links to cardiovascular diseases. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 302: H2148–2165. - PubMed
-
- Vendramini-Costa DB, Carvalho JE (2012) Molecular Link Mechanisms between Inflammation and Cancer. Curr Pharm Des 18: 3831–3852. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

