Controlling natural killer cell responses: integration of signals for activation and inhibition
- PMID: 23516982
- PMCID: PMC3868343
- DOI: 10.1146/annurev-immunol-020711-075005
Controlling natural killer cell responses: integration of signals for activation and inhibition
Abstract
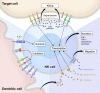
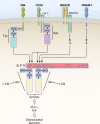
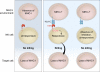
Understanding how signals are integrated to control natural killer (NK) cell responsiveness in the absence of antigen-specific receptors has been a challenge, but recent work has revealed some underlying principles that govern NK cell responses. NK cells use an array of innate receptors to sense their environment and respond to alterations caused by infections, cellular stress, and transformation. No single activation receptor dominates; instead, synergistic signals from combinations of receptors are integrated to activate natural cytotoxicity and cytokine production. Inhibitory receptors for major histocompatibility complex class I (MHC-I) have a critical role in controlling NK cell responses and, paradoxically, in maintaining NK cells in a state of responsiveness to subsequent activation events, a process referred to as licensing. MHC-I-specific inhibitory receptors both block activation signals and trigger signals to phosphorylate and inactivate the small adaptor Crk. These different facets of inhibitory signaling are incorporated into a revocable license model for the reversible tuning of NK cell responsiveness.
Figures

References
-
- Tassi I, Klesney-Tait J, Colonna M. Dissecting natural killer cell activation pathways through analysis of genetic mutations in human and mouse. Immunol. Rev. 2006;214:92–-105. - PubMed
-
- Bryceson YT, Chiang SC, Darmanin S, Fauriat C, Schlums H, et al. Molecular mechanisms of natural killer cell activation. J. Innate Immun. 2011;3:216–-26. - PubMed
-
- Kim S, Poursine-Laurent J, Truscott SM, Lybarger L, Song YJ, et al. Licensing of natural killer cells by host major histocompatibility complex class I molecules. Nature. 2005;436:709–-13. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

