Metal-free α-amination of secondary amines: computational and experimental evidence for azaquinone methide and azomethine ylide intermediates
- PMID: 23517448
- PMCID: PMC3654248
- DOI: 10.1021/jo400483h
Metal-free α-amination of secondary amines: computational and experimental evidence for azaquinone methide and azomethine ylide intermediates
Abstract
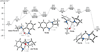
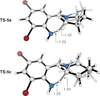
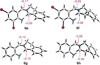
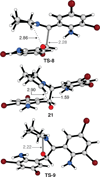
We have performed a combined computational and experimental study to elucidate the mechanism of a metal-free α-amination of secondary amines. Calculations predicted azaquinone methides and azomethine ylides as the reactive intermediates and showed that iminium ions are unlikely to participate in these transformations. These results were confirmed by experimental deuterium-labeling studies and the successful trapping of the postulated azomethine ylide and azaquinone methide intermediates. In addition, computed barrier heights for the rate-limiting step correlate qualitatively with experimental findings.
Figures
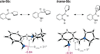


References
-
- Hiersemann M. In: Comprehensive Organic Functional Group Transformations II. Katritzky ART, Richard JK, editors. Vol. 4. Oxford, UK: Elsevier Ltd.; 2005. p. 411.
-
-
For selected examples of aminal-containing natural products, see: Hino T, Nakagawa M. Alkaloids. Vol. 34. New York: Academic Press; 1988. p. 1. Hubbs JL, Heathcock CH. Org. Lett. 1999;1:1315. Snider BB, Zeng HB. Org. Lett. 2002;4:1087. Movassaghi M, Schmidt MA. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2007;46:3725. Crich D, Banerjee A. Acc. Chem. Res. 2007;40:151. Kuroda T, Kigoshi H. Org. Lett. 2008;10:489. Wang SH, Romo D. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2008;47:1284. Dounay AB, Humphreys PG, Overman LE, Wrobleski AD. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008;130:5368. Pham V, Jossang A, Grellier P, Sevenet T, Nguyen V, Bodo B. J. Org. Chem. 2008;73:7565. Zhang M, Huang XP, Shen LQ, Qin Y. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009;131:6013.
-
-
- Zhang C, De CK, Mal R, Seidel D. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008;130:416. - PubMed
- Zhang C, De CK, Seidel D. Org. Synth. 2012;89:274.
-
-
For related studies, see: Cohen N, Blount JF, Lopresti RJ, Trullinger DP. J. Org. Chem. 1979;44:4005. Zheng L, Yang F, Dang Q, Bai X. Org. Lett. 2008;10:889. Polshettiwar V, Varma RS. Tetrahedron Lett. 2008;49:7165. Bi HP, Zhao L, Liang YM, Li CJ. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009;48:792. Bi HP, Chen WW, Liang YM, Li CJ. Org. Lett. 2009;11:3246. Bi HP, Teng Q, Guan M, Chen WW, Liang YM, Yao X, Li CJ. J. Org. Chem. 2010;75:783.
-
-
-
The term redox-neutral refers to the fact that this transformation does not require a terminal oxidant. For reviews on redox-economy, see: Burns NZ, Baran PS, Hoffmann RW. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009;48:2854. Newhouse T, Baran PS, Hoffmann RW. Chem. Soc. Rv. 2009;38:3010.
-
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

