Stereotactic body radiotherapy using gated radiotherapy with real-time tumor-tracking for stage I non-small cell lung cancer
- PMID: 23518013
- PMCID: PMC3614446
- DOI: 10.1186/1748-717X-8-69
Stereotactic body radiotherapy using gated radiotherapy with real-time tumor-tracking for stage I non-small cell lung cancer
Abstract
Background: To clarify the clinical outcomes of two dose schedule of stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT) for stage I non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) using a real-time tumor-tracking radiation therapy (RTRT) system in single institution.
Methods: Using a superposition algorithm, we administered 48 Gy in 4 fractions at the isocenter in 2005-2006 and 40 Gy in 4 fractions to the 95% volume of PTV in 2007-2010 with a treatment period of 4 to 7 days. Target volume margins were fixed irrespective of the tumor amplitude.
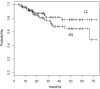
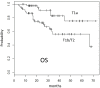
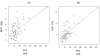
Results: In total, 109 patients (79 T1N0M0 and 30 T2N0M0). With a median follow-up period of 25 months (range, 4 to 72 months), the 5-year local control rate (LC) was 78% and the 5-year overall survival rate (OS) was 64%. Grade 2, 3, 4, and 5 radiation pneumonitis (RP) was experienced by 15 (13.8%), 3 (2.8%), 0, and 0 patients, respectively. The mean lung dose (MLD) and the volume of lung receiving 20 Gy (V20) were significantly higher in patients with RP Grade 2/3 than in those with RP Grade 0/1 (MLD p = 0.002, V20 p = 0.003). There was no correlation between larger maximum amplitude of marker movement and larger PTV (r = 0.137), MLD (r = 0.046), or V20 (r = 0.158).
Conclusions: SBRT using the RTRT system achieved LC and OS comparable to other SBRT studies with very low incidence of RP, which was consistent with the small MLD and V20 irrespective of tumor amplitude. For stage I NSCLC, SBRT using RTRT was suggested to be reliable and effective, especially for patients with large amplitude of tumor movement.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Clinical outcomes of stage I and IIA non-small cell lung cancer patients treated with stereotactic body radiotherapy using a real-time tumor-tracking radiotherapy system.Radiat Oncol. 2017 Jan 5;12(1):3. doi: 10.1186/s13014-016-0742-3. Radiat Oncol. 2017. PMID: 28057036 Free PMC article.
-
A dose-volume analysis of radiation pneumonitis in non-small cell lung cancer patients treated with stereotactic body radiation therapy.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2012 Jan 1;82(1):457-62. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2010.08.056. Epub 2010 Oct 29. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2012. PMID: 21035956
-
Assessment of Monte Carlo algorithm for compliance with RTOG 0915 dosimetric criteria in peripheral lung cancer patients treated with stereotactic body radiotherapy.J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2016 May 8;17(3):277-293. doi: 10.1120/jacmp.v17i3.6077. J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2016. PMID: 27167284 Free PMC article.
-
Local Control After Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy for Stage I Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2021 May 1;110(1):160-171. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2019.03.045. Epub 2019 Apr 5. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2021. PMID: 30954520 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Stereotactic radiotherapy for lung cancer].Bull Cancer. 2025 Mar;112(3S1):3S31-3S38. doi: 10.1016/S0007-4551(25)00155-9. Bull Cancer. 2025. PMID: 40155075 Review. French.
Cited by
-
Combined radio- and chemotherapy for non-small cell lung cancer: systematic review of landmark studies based on acquired citations.Front Oncol. 2013 Jul 9;3:176. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2013.00176. eCollection 2013. Front Oncol. 2013. PMID: 23847765 Free PMC article.
-
Re-evaluating the risk factors for radiation pneumonitis in the era of immunotherapy.J Transl Med. 2023 Jun 7;21(1):368. doi: 10.1186/s12967-023-04212-5. J Transl Med. 2023. PMID: 37287014 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Predicting risk factors for radiation pneumonitis after stereotactic body radiation therapy for primary or metastatic lung tumours.Br J Radiol. 2017 May;90(1073):20160508. doi: 10.1259/bjr.20160508. Epub 2017 Apr 6. Br J Radiol. 2017. PMID: 28195507 Free PMC article.
-
Outcome and toxicity of stereotactic body radiotherapy with helical tomotherapy for inoperable lung tumor: analysis of Grade 5 radiation pneumonitis.J Radiat Res. 2014 May;55(3):575-82. doi: 10.1093/jrr/rrt146. Epub 2014 Jan 23. J Radiat Res. 2014. PMID: 24457315 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Clinical outcome of hypofractionated breath-hold image-guided SABR of primary lung tumors and lung metastases.Radiat Oncol. 2014 Jan 8;9:10. doi: 10.1186/1748-717X-9-10. Radiat Oncol. 2014. PMID: 24401323 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baumann P, Nyman J, Hoyer M, Wennberg B, Gagliardi G, Lax I, Drugge N, Ekberg L, Friesland S, Johansson K-A, Lund J-A, Morhed E, Nilsson K, Levin N, Paludan M, Sederholm C, Traberg A, Wittgren L, Lewensohn R. Outcome in a prospective phase II trial of medically inoperable stage I non-small-cell lung cancer patients treated with stereotactic body radiotherapy. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27:3290–3296. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2008.21.5681. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Onishi H, Shirato H, Nagata Y, Hiraoka M, Fujino M, Gomi K, Niibe Y, Karasawa K, Hayakawa K, Takai Y, Kimura T, Takeda A, Ouchi A, Hareyama M, Kokubo M, Hara R, Itami J, Yamada K, Araki T. Hypofractionated stereotactic radiotherapy (HypoFXSRT) for stage I non-small cell lung cancer: updated results of 257 patients in a Japanese multi-institutional study. J Thorac Oncol. 2007;2:S94–S100. doi: 10.1097/JTO.0b013e318074de34. - DOI - PubMed
-
- George R, Chung TD, Vedam SS, Ramakrishnan V, Mohan R, Weiss E, Keall PJ. Audio-visual biofeedback for respiratory-gated radiotherapy: impact of audio instruction and audio-visual biofeedback on respiratory-gated radiotherapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2006;65:924–933. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2006.02.035. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Onishi H, Shirato H, Nagata Y, Hiraoka M, Fujino M, Gomi K, Karasawa K, Hayakawa K, Niibe Y, Takai Y, Kimura T, Takeda A, Ouchi A, Hareyama M, Kokubo M, Kozuka T, Arimoto T, Hara R, Itami J, Araki T. Stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT) for operable stage I Non-small-cell lung cancer: Can SBRT Be comparable to surgery? Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2010;81:1352–1358. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

