Regulation of c-Myc ubiquitination controls chronic myelogenous leukemia initiation and progression
- PMID: 23518350
- PMCID: PMC3609428
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ccr.2013.01.025
Regulation of c-Myc ubiquitination controls chronic myelogenous leukemia initiation and progression
Abstract
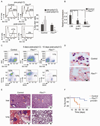
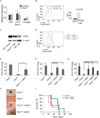
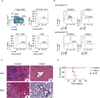
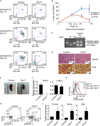
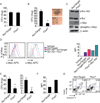
The molecular mechanisms regulating leukemia-initiating cell (LIC) function are of important clinical significance. We use chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML) as a model of LIC-dependent malignancy and identify the interaction between the ubiquitin ligase Fbw7 and its substrate c-Myc as a regulator of LIC homeostasis. Deletion of Fbw7 leads to c-Myc overexpression, p53-dependent LIC-specific apoptosis, and the eventual inhibition of tumor progression. A decrease of either c-Myc protein levels or attenuation of the p53 response rescues LIC activity and disease progression. Further experiments showed that Fbw7 expression is required for survival and maintenance of human CML LIC. These studies identify a ubiquitin ligase:substrate pair regulating LIC activity, suggesting that targeting of the Fbw7:c-Myc axis is an attractive therapy target in refractory CML.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

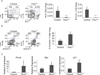

References
-
- Bartram CR, de Klein A, Hagemeijer A, van Agthoven T, Geurts van Kessel A, Bootsma D, Grosveld G, Ferguson-Smith MA, Davies T, Stone M, et al. Translocation of c-ab1 oncogene correlates with the presence of a Philadelphia chromosome in chronic myelocytic leukaemia. Nature. 1983;306:277–280. - PubMed
-
- Bhatia R, Holtz M, Niu N, Gray R, Snyder DS, Sawyers CL, Arber DA, Slovak ML, Forman SJ. Persistence of malignant hematopoietic progenitors in chronic myelogenous leukemia patients in complete cytogenetic remission following imatinib mesylate treatment. Blood. 2003;101:4701–4707. - PubMed
-
- Bonnet D, Dick JE. Human acute myeloid leukemia is organized as a hierarchy that originates from a primitive hematopoietic cell. Nat Med. 1997;3:730–737. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 1R01CA173636/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA173636/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01CA133379/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 1T32CA160002-01/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA149655/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA105129/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- HHMI/Howard Hughes Medical Institute/United States
- R01GM088847/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- 5T32HL007151-33/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01CA149655/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 CA160002/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01CA105129/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM088847/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA133379/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HL007151/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

