A multidisciplinary clinical program is effective in stabilizing BMI and reducing transaminase levels in pediatric patients with NAFLD
- PMID: 23518484
- PMCID: PMC3696482
- DOI: 10.1097/MPG.0b013e318290d138
A multidisciplinary clinical program is effective in stabilizing BMI and reducing transaminase levels in pediatric patients with NAFLD
Abstract
Background and aim: Weight loss is an effective treatment for children with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), but it is extremely difficult to achieve outside of an intensive weight management program. We hypothesized that one can achieve success in improving NAFLD and weight-related outcomes in a structured and focused multidisciplinary clinical program feasible to implement in a gastroenterology clinic.
Methods: We prospectively tracked the clinical status of our patients enrolled in a multidisciplinary program of dietary and exercise advice through an institutional review board-approved NAFLD registry. Each patient met with a gastroenterologist and dietitian every 3 months for 30 minutes to set individualized goals and monitor progress.
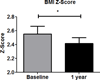
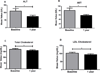
Results: A total of 108 children have been enrolled in the registry, and of the 83 that were eligible for 1-year follow-up and included in the analysis, 39 patients returned, resulting in a 47% follow-up rate. These 39 patients showed statistically significant improvements in mean BMI z score (-0.1 U, P < 0.05), total (-11 mg/dL, P < 0.05) and low-density lipoprotein (9 mg/dL, P < 0.05) cholesterol, and serum alanine aminotransferase levels (-36 U/L) and aspartate aminotransferase levels (-22 U/L) levels.
Conclusions: A clinically feasible multidisciplinary program for obese pediatric patients with NAFLD stabilized BMI z score and significantly improved aminotransferase levels at 1-year follow-up.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- DeMaria EJ. Bariatric surgery for morbid obesity. N Engl J Med. 2007;356(21):2176–2183. - PubMed
-
- Mummadi RR, Kasturi KS, Chennareddygari S, et al. Effect of bariatric surgery on nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2008;6(12):1396–1402. - PubMed
-
- Buchwald H, Avidor Y, Braunwald E, et al. Bariatric surgery: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Jama. 2004;292(14):1724–1737. - PubMed
-
- Taha D. Hyperlipidemia in children with type 2 diabetes mellitus. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2002;15(Suppl 1):505–507. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous