Hepatitis B surface antigen levels: association with 5-year response to peginterferon alfa-2a in hepatitis B e-antigen-negative patients
- PMID: 23518903
- PMCID: PMC3601258
- DOI: 10.1007/s12072-012-9343-x
Hepatitis B surface antigen levels: association with 5-year response to peginterferon alfa-2a in hepatitis B e-antigen-negative patients
Abstract
Purpose: To investigate the durability of response to peginterferon alfa-2a up to 5 years post-treatment and factors associated with response in hepatitis B e-antigen (HBeAg)-negative patients.
Methods: HBeAg-negative patients received peginterferon alfa-2a (180 μg/week) ± lamivudine (100 mg/day) for 48 weeks as part of a multicenter, randomized study. The planned 5-year efficacy analysis included patients (n = 230) enrolled in the long-term follow-up study. On-treatment hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) decline kinetics were analyzed retrospectively in a subgroup of patients with HBsAg data available at baseline, weeks 12, 24, and 48 on-treatment, and 6 months post-treatment (n = 120). Receiver operating characteristic analyses identified the on-treatment HBsAg levels associated with response at 1 and 5 years post-treatment.
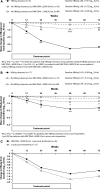
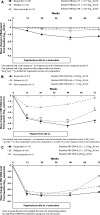
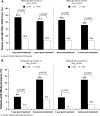
Results: HBV DNA ≤2,000 IU/mL and HBsAg clearance at 5 years post-treatment were achieved by 23 and 12% of patients, respectively. High rates of HBsAg clearance at 5 years post-treatment were achieved by patients with HBV DNA ≤2,000 IU/mL at 1 year post-treatment (28%). Rates of HBV DNA ≤2,000 IU/mL at 1 year post-treatment were 47.2 and 43.4% in patients with ≥10% decline from baseline at weeks 12 and 24, respectively, compared with 16.4% (p = 0.0003) and 13.2% (p < 0.0004) in patients with a <10% decline. Rates of HBsAg clearance at 5 years post-treatment were 22.6 and 22.4% in patients with ≥10% decline at weeks 12 and 24, respectively, compared with 7.5% (p = 0.0161) and 3.8% (p < 0.0001) in patients with <10% decline.
Conclusions: Peginterferon alfa-2a results in increasing rates of HBsAg clearance during post-treatment follow-up in HBeAg-negative patients. On-treatment decline in HBsAg is significantly associated with long-term post-treatment response.
Keywords: Chronic hepatitis B; HBV DNA suppression; HBsAg clearance; Long-term response; Prediction.
Figures
References
-
- Lok AS, McMahon BJ. Chronic hepatitis B: update 2009. Hepatology. 2009;50:1–36. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

