Cell-cycle specific association of transcription factors and RNA polymerase ii with the human β-globin gene locus
- PMID: 23519692
- PMCID: PMC3744833
- DOI: 10.1002/jcb.24542
Cell-cycle specific association of transcription factors and RNA polymerase ii with the human β-globin gene locus
Abstract
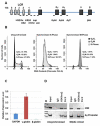
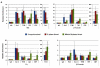
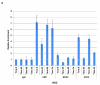
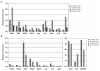
The human β-globin genes are regulated by a locus control region (LCR) and are expressed at extremely high levels in erythroid cells. How transcriptional fidelity of highly expressed genes is regulated and maintained during the cell cycle is not completely understood. Here, we analyzed the association of transcription factor USF, the co-activator CBP, topoisomerase I (Topo I), basal transcription factor TFIIB, and RNA polymerase II (Pol II) with the β-globin gene locus at specific cell-cycle stages. The data demonstrate that while association of Pol II with globin locus associated chromatin decreased in mitotically arrested cells, it remained bound at lower levels at the γ-globin gene promoter. During early S-phase, association of CBP, USF, and Pol II with the globin gene locus decreased. The re-association of CBP and USF2 with the LCR preceded re-association of Pol II, suggesting that these proteins together mediate recruitment of Pol II to the β-globin gene locus during S-phase. Finally, we analyzed the association of Topo I with the globin gene locus during late S-phase. In general, Topo I association correlated with the binding of Pol II. Inhibition of Topo I activity reduced Pol II binding at the LCR and intergenic regions but not at the γ-globin gene promoter. The data demonstrate dynamic associations of transcription factors with the globin gene locus during the cell cycle and support previous results showing that specific components of transcription complexes remain associated with highly transcribed genes during mitosis.
Keywords: CELL CYCLE; GLOBIN GENE LOCUS; MITOSIS; RNA POLYMERASE II; TRANSCRIPTION FACTOR.
Copyright © 2013 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures

Similar articles
-
USF and NF-E2 cooperate to regulate the recruitment and activity of RNA polymerase II in the beta-globin gene locus.J Biol Chem. 2010 May 21;285(21):15894-905. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.098376. Epub 2010 Mar 17. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20236933 Free PMC article.
-
Dissecting the function of the adult β-globin downstream promoter region using an artificial zinc finger DNA-binding domain.Nucleic Acids Res. 2014 Apr;42(7):4363-74. doi: 10.1093/nar/gku107. Epub 2014 Feb 4. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014. PMID: 24497190 Free PMC article.
-
Recruitment of transcription complexes to the beta-globin gene locus in vivo and in vitro.J Biol Chem. 2004 Nov 26;279(48):50350-7. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M408883200. Epub 2004 Sep 22. J Biol Chem. 2004. PMID: 15385559 Free PMC article.
-
Chromatin loop formation in the β-globin locus and its role in globin gene transcription.Mol Cells. 2012 Jul;34(1):1-5. doi: 10.1007/s10059-012-0048-8. Epub 2012 May 18. Mol Cells. 2012. PMID: 22610406 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Joining the loops: beta-globin gene regulation.IUBMB Life. 2008 Dec;60(12):824-33. doi: 10.1002/iub.129. IUBMB Life. 2008. PMID: 18767169 Review.
Cited by
-
DNA topology and transcription.Nucleus. 2014 May-Jun;5(3):195-202. doi: 10.4161/nucl.28909. Epub 2014 Apr 22. Nucleus. 2014. PMID: 24755522 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Amrolia PJ, Ramamurthy L, Saluja D, Tanese N, Jane SM, Cunningham JM. The activation domain of the enhancer binding protein p45NF-E2 interacts with TAFII130 and mediates long-range activation of the alpha- and beta-globin gene loci in an erythroid cell line. Proc Nat Acad Sci USA. 1997;94:10051–10056. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bermejo R, Capra T, Gonzales-Huici V, Fachinetti D, Cocito A, Natoli G, Katou Y, Mori H, Kurokawa K, Shirahige K, Foiani M. Genome-organizing factors Top2 and Hmo1 prevent chromosome fragility at sites of S-phase transcription. Cell. 2009;123:870–884. - PubMed
-
- Bulger M, Groudine M. Looping versus linking: toward a model for long-distance gene activation. Genes Dev. 1999;13:2465–77. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

