Temsirolimus combined with sorafenib in hepatocellular carcinoma: a phase I dose-finding trial with pharmacokinetic and biomarker correlates
- PMID: 23519998
- PMCID: PMC3690907
- DOI: 10.1093/annonc/mdt109
Temsirolimus combined with sorafenib in hepatocellular carcinoma: a phase I dose-finding trial with pharmacokinetic and biomarker correlates
Abstract
Background: Based upon preclinical evidence for improved antitumor activity in combination, this phase I study investigated the maximum-tolerated dose (MTD), safety, activity, pharmacokinetics (PK), and biomarkers of the mammalian target of rapamycin inhibitor, temsirolimus, combined with sorafenib in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).
Patients and methods: Patients with incurable HCC and Child Pugh score ≤B7 were treated with sorafenib plus temsirolimus by 3 + 3 design. The dose-limiting toxicity (DLT) interval was 28 days. The response was assessed every two cycles. PK of temsirolimus was measured in a cohort at MTD.
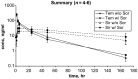
Results: Twenty-five patients were enrolled. The MTD was temsirolimus 10 mg weekly plus sorafenib 200 mg twice daily. Among 18 patients at MTD, DLT included grade 3 hand-foot skin reaction (HFSR) and grade 3 thrombocytopenia. Grade 3 or 4 related adverse events at MTD included hypophosphatemia (33%), infection (22%), thrombocytopenia (17%), HFSR (11%), and fatigue (11%). With sorafenib, temsirolimus clearance was more rapid (P < 0.05). Two patients (8%) had a confirmed partial response (PR); 15 (60%) had stable disease (SD). Alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) declined ≥50% in 60% assessable patients.
Conclusion: The MTD of sorafenib plus temsirolimus in HCC was lower than in other tumor types. HCC-specific phase I studies are necessary. The observed efficacy warrants further study.
Keywords: hepatocellular carcinoma; mTOR; pharmacokinetics; sorafenib; temsirolimus.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Phase I study investigating everolimus combined with sorafenib in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma.J Hepatol. 2013 Dec;59(6):1271-7. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2013.07.029. Epub 2013 Aug 6. J Hepatol. 2013. PMID: 23928403 Clinical Trial.
-
A phase Ib study of selumetinib (AZD6244, ARRY-142886) in combination with sorafenib in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).Ann Oncol. 2016 Dec;27(12):2210-2215. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdw415. Epub 2016 Sep 28. Ann Oncol. 2016. PMID: 27681866 Clinical Trial.
-
Effects of sorafenib combined with low-dose interferon therapy for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: a pilot study.Int J Clin Oncol. 2016 Aug;21(4):676-683. doi: 10.1007/s10147-015-0942-0. Epub 2015 Dec 23. Int J Clin Oncol. 2016. PMID: 26701173
-
Adverse events affect sorafenib efficacy in patients with recurrent hepatocellular carcinoma after liver transplantation: experience at a single center and review of the literature.Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2013 Feb;25(2):180-6. doi: 10.1097/MEG.0b013e328359e550. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2013. PMID: 23044808 Review.
-
Sorafenib: a review of its use in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma.Drugs. 2009;69(2):223-40. doi: 10.2165/00003495-200969020-00006. Drugs. 2009. PMID: 19228077 Review.
Cited by
-
Dosing de novo combinations of two targeted drugs: Towards a customized precision medicine approach to advanced cancers.Oncotarget. 2016 Mar 8;7(10):11310-20. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.7023. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 26824502 Free PMC article.
-
Advanced Hepatocellular Cancer: the Current State of Future Research.Curr Treat Options Oncol. 2016 Aug;17(8):43. doi: 10.1007/s11864-016-0415-3. Curr Treat Options Oncol. 2016. PMID: 27344158 Review.
-
Management of recurrent hepatocellular carcinoma after liver transplant.World J Hepatol. 2015 May 18;7(8):1142-8. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v7.i8.1142. World J Hepatol. 2015. PMID: 26052403 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epigenetics in hepatocellular carcinoma: an update and future therapy perspectives.World J Gastroenterol. 2014 Jan 14;20(2):333-45. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i2.333. World J Gastroenterol. 2014. PMID: 24574704 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Microtubule-targeting agents in oncology and therapeutic potential in hepatocellular carcinoma.Onco Targets Ther. 2014 Apr 16;7:575-85. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S46019. eCollection 2014. Onco Targets Ther. 2014. PMID: 24790457 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Llovet JM, Ricci S, Mazzaferro V, et al. Sorafenib in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2008;359:378–390. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa0708857. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Cheng A, Kang Y, Lin D, Park J, et al. Phase III trial of sunitinib (Su) versus sorafenib (So) in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). In American Society of Clinical Oncology Annual Meeting. Chicago, IL. J Clin Oncol. 2011 29(15-suppl): 4000.
-
- Llovet JM, Decaen T, Raoul J-L, Boucher E, et al. Brivanib versus placebo in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) who failed or were intolerant to sorafenib: results from the phase 3 BRISK-PS study. International Liver Congress, European Association for the Study of the Liver; Barcelona, Spain. 2012.
-
- Zhu RO, Evans J, Ross P, et al. SEARCH: A phase III, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of sorafenib plus erlotinib in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). 37th ESMO Congress, European Society of Medical Oncology; Vienna, Austria. 2012. - PubMed
-
- Menon S, Yecies JL, Zhang HH, et al. Chronic activation of mTOR complex 1 is sufficient to cause hepatocellular carcinoma in mice. Sci Signal. 2012;5:ra24. doi:10.1126/scisignal.2002739. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

