The challenge of cholangiocarcinoma: dissecting the molecular mechanisms of an insidious cancer
- PMID: 23520144
- PMCID: PMC3597011
- DOI: 10.1242/dmm.010561
The challenge of cholangiocarcinoma: dissecting the molecular mechanisms of an insidious cancer
Abstract
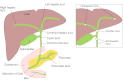
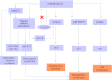
Cholangiocarcinoma is a fatal cancer of the biliary epithelium and has an incidence that is increasing worldwide. Survival beyond a year of diagnosis is less than 5%, and therapeutic options are few. Known risk factors include biliary diseases such as primary sclerosing cholangitis and parasitic infestation of the biliary tree, but most cases are not associated with any of these underlying diseases. Numerous in vitro and in vivo models, as well as novel analytical techniques for human samples, are helping to delineate the many pathways implicated in this disease, albeit at a frustratingly slow pace. As yet, however, none of these studies has been translated into improved patient outcome and, overall, the pathophysiology of cholangiocarcinoma is still poorly understood. There remains an urgent need for new approaches and models to improve management of this insidious and devastating disease. In this review, we take a bedside-to-bench approach to discussing cholangiocarcinoma and outline research opportunities for the future in this field.
Figures
References
-
- Abdel Wahab M., Mostafa M., Salah T., Fouud A., Kandeel T., Elshobary M., Abd Allah O. F., Elghawalby N., Sultan A., Ezzat F. (2007). Epidemiology of hilar cholangiocarcinoma in Egypt: single center study. Hepatogastroenterology 54, 1626-1631 - PubMed
-
- Ahrendt S. A., Rashid A., Chow J. T., Eisenberger C. F., Pitt H. A., Sidransky D. (2000). p53 overexpression and K-ras gene mutations in primary sclerosing cholangitis-associated biliary tract cancer. J. Hepatobiliary Pancreat. Surg. 7, 426-431 - PubMed
-
- Alpini G., Kanno N., Phinizy J. L., Glaser S., Francis H., Taffetani S., LeSage G. (2004). Tauroursodeoxycholate inhibits human cholangiocarcinoma growth via Ca2+-, PKC-, and MAPK-dependent pathways. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 286, G973-G982 - PubMed
-
- Bangarulingam S. Y., Bjornsson E., Enders F., Barr Fritcher E. G., Gores G., Halling K. C., Lindor K. D. (2010). Long-term outcomes of positive fluorescence in situ hybridization tests in primary sclerosing cholangitis. Hepatology 51, 174-180 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

