Multiple sites of the cleavage of 21- and 25-mer encephalytogenic oligopeptides corresponding to human myelin basic protein (MBP) by specific anti-MBP antibodies from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus
- PMID: 23520443
- PMCID: PMC3592856
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0051600
Multiple sites of the cleavage of 21- and 25-mer encephalytogenic oligopeptides corresponding to human myelin basic protein (MBP) by specific anti-MBP antibodies from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus
Abstract
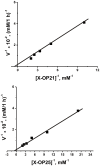
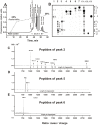
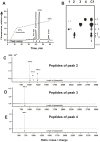
IgGs from patients with multiple sclerosis and systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) purified on MBP-Sepharose in contrast to canonical proteases hydrolyze effectively only myelin basic protein (MBP), but not many other tested proteins. Here we have shown for the first time that anti-MBP SLE IgGs hydrolyze nonspecific tri- and tetrapeptides with an extreme low efficiency and cannot effectively hydrolyze longer 20-mer nonspecific oligopeptides corresponding to antigenic determinants (AGDs) of HIV-1 integrase. At the same time, anti-MBP SLE IgGs efficiently hydrolyze oligopeptides corresponding to AGDs of MBP. All sites of IgG-mediated proteolysis of 21-and 25-mer encephalytogenic oligopeptides corresponding to two known AGDs of MBP were found by a combination of reverse-phase chromatography, TLC, and MALDI spectrometry. Several clustered major, moderate, and minor sites of cleavage were revealed in the case of 21- and 25-mer oligopeptides. The active sites of anti-MBP abzymes are localised on their light chains, while heavy chains are responsible for the affinity of protein substrates. Interactions of intact globular proteins with both light and heavy chains of abzymes provide high affinity to MBP and specificity of this protein hydrolysis. The affinity of anti-MBP abzymes for intact MBP is approximately 1000-fold higher than for the oligopeptides. The data suggest that all oligopeptides interact mainly with the light chains of different monoclonal abzymes of total pool of IgGs, which possesses a lower affinity for substrates, and therefore, depending on the oligopeptide sequences, their hydrolysis may be less specific than globular protein and can occur in several sites.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



Similar articles
-
Multiple sites of the cleavage of 17- and 19-mer encephalytogenic oligopeptides corresponding to human myelin basic protein (MBP) by specific anti-MBP antibodies from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus.Peptides. 2012 Sep;37(1):69-78. doi: 10.1016/j.peptides.2012.07.003. Epub 2012 Jul 7. Peptides. 2012. PMID: 22781164
-
Why specific anti-integrase antibodies from HIV-infected patients can efficiently hydrolyze 21-mer oligopeptide corresponding to antigenic determinant of human myelin basic protein.J Mol Recognit. 2014 Jan;27(1):32-45. doi: 10.1002/jmr.2329. J Mol Recognit. 2014. PMID: 24375582
-
Specific anti-integrase abzymes from HIV-infected patients: a comparison of the cleavage sites of intact globular HIV integrase and two 20-mer oligopeptides corresponding to its antigenic determinants.J Mol Recognit. 2013 Mar;26(3):121-35. doi: 10.1002/jmr.2253. J Mol Recognit. 2013. PMID: 23345103
-
Immune Response and Production of Abzymes in Patients with Autoimmune and Neurodegenerative Diseases.Biochemistry (Mosc). 2025 Jan;90(Suppl 1):S373-S400. doi: 10.1134/S0006297924604167. Biochemistry (Mosc). 2025. PMID: 40164167 Review.
-
Autoantibodies with enzymatic properties in human autoimmune diseases.J Autoimmun. 2011 Sep;37(2):144-50. doi: 10.1016/j.jaut.2011.05.007. Epub 2011 May 31. J Autoimmun. 2011. PMID: 21624820 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Multiple Sclerosis: Enzymatic Cross Site-Specific Recognition and Hydrolysis of H2A Histone by IgGs against H2A, H1, H2B, H3 Histones, Myelin Basic Protein, and DNA.Biomedicines. 2022 Aug 3;10(8):1876. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10081876. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 36009424 Free PMC article.
-
HIV-Infected Patients: Cross Site-Specific Hydrolysis of H2a and H2b Histones and Myelin Basic Protein with Antibodies against These Three Proteins.Biomolecules. 2020 Oct 30;10(11):1501. doi: 10.3390/biom10111501. Biomolecules. 2020. PMID: 33143355 Free PMC article.
-
Natural IgG against S-Protein and RBD of SARS-CoV-2 Do Not Bind and Hydrolyze DNA and Are Not Autoimmune.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Nov 8;23(22):13681. doi: 10.3390/ijms232213681. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36430159 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and characterization of antigen-specific CD4+ T cells targeting renally expressed antigens in human lupus nephritis with two independent methods.Sci Rep. 2020 Dec 4;10(1):21312. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-78223-3. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 33277543 Free PMC article.
-
HIV-Infected Patients: Cross Site-Specific Hydrolysis of H3 and H4 Histones and Myelin Basic Protein with Antibodies against These Three Proteins.Molecules. 2021 Jan 9;26(2):316. doi: 10.3390/molecules26020316. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 33435385 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Keinan E ed (2005) Catalytic antibodies: Weinheim, Germany: Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH and Co. KgaA. p. 1–586
-
- Nevinsky GA, Buneva VN (2002) Human catalytic RNA- and DNA-hydrolyzing antibodies. J Immunol Methods 269: 235–249. - PubMed
-
- Nevinsky GA, Favorova OO, Buneva VN (2002) Natural Catalytic Antibodies-New Characters in the Protein Repertoire. In: Golemis E editor. Protein-protein interactions; a molecular cloning manual. New York: Cold Spring Harbor Lab. Press, pp. 1–523.
-
- Nevinsky GA, Buneva VN (2005) Natural catalytic antibodies-abzymes. In: Keinan E editor. Catalytic antibodies. Weinheim, Germany: VCH-Wiley press. pp. 503–567.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

