Local synchronization of resting-state dynamics encodes Gray's trait Anxiety
- PMID: 23520499
- PMCID: PMC3592924
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0058336
Local synchronization of resting-state dynamics encodes Gray's trait Anxiety
Abstract
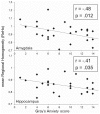
The Behavioral Inhibition System (BIS) as defined within the Reinforcement Sensitivity Theory (RST) modulates reactions to stimuli indicating aversive events. Gray's trait Anxiety determines the extent to which stimuli activate the BIS. While studies have identified the amygdala-septo-hippocampal circuit as the key-neural substrate of this system in recent years and measures of resting-state dynamics such as randomness and local synchronization of spontaneous BOLD fluctuations have recently been linked to personality traits, the relation between resting-state dynamics and the BIS remains unexplored. In the present study, we thus examined the local synchronization of spontaneous fMRI BOLD fluctuations as measured by Regional Homogeneity (ReHo) in the hippocampus and the amygdala in twenty-seven healthy subjects. Correlation analyses showed that Gray's trait Anxiety was significantly associated with mean ReHo in both the amygdala and the hippocampus. Specifically, Gray's trait Anxiety explained 23% and 17% of resting-state ReHo variance in the left amygdala and the left hippocampus, respectively. In summary, we found individual differences in Gray's trait Anxiety to be associated with ReHo in areas previously associated with BIS functioning. Specifically, higher ReHo in resting-state neural dynamics corresponded to lower sensitivity to punishment scores both in the amygdala and the hippocampus. These findings corroborate and extend recent findings relating resting-state dynamics and personality while providing first evidence linking properties of resting-state fluctuations to Gray's BIS.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Gray JA (1982) The neuropsychology of anxiety: An enquiry into the functions of the septo-hippocampal system. Oxford: Oxford University Press.
-
- Corr PJ (2008) The Reinforcement Sensitivity Theory of Personality. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
-
- Gray JA, McNaughton N (2000) The neuropsychology of anxiety: An enquiry into the functions of the septo-hippocampal system. Oxford: Oxford University Press.
-
- Gray JA (1991) The neuropsychology of temperament. In: Strelau J, Angleitner A, editors. Explorations in temperament. New York: Plenum. 105–128.
-
- Barros-Loscertales A, Meseguer V, Sanjuan A, Belloch V, Parcet MA, et al. (2006) Behavioral Inhibition System activity is associated with increased amygdala and hippocampal gray matter volume: A voxel-based morphometry study. NeuroImage 33: 1011–1015. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous