The proton-pump inhibitor lansoprazole enhances amyloid beta production
- PMID: 23520537
- PMCID: PMC3592824
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0058837
The proton-pump inhibitor lansoprazole enhances amyloid beta production
Abstract
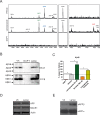
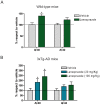
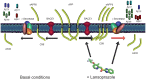
A key event in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease (AD) is the accumulation of amyloid-β (Aβ) species in the brain, derived from the sequential cleavage of the amyloid precursor protein (APP) by β- and γ-secretases. Based on a systems biology study to repurpose drugs for AD, we explore the effect of lansoprazole, and other proton-pump inhibitors (PPIs), on Aβ production in AD cellular and animal models. We found that lansoprazole enhances Aβ37, Aβ40 and Aβ42 production and lowers Aβ38 levels on amyloid cell models. Interestingly, acute lansoprazole treatment in wild type and AD transgenic mice promoted higher Aβ40 levels in brain, indicating that lansoprazole may also exacerbate Aβ production in vivo. Overall, our data presents for the first time that PPIs can affect amyloid metabolism, both in vitro and in vivo.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Hardy J, Selkoe DJ (2002) The amyloid hypothesis of Alzheimer's disease: progress and problems on the road to therapeutics. Science 297: 353–356. - PubMed
-
- Querfurth HW, LaFerla FM (2010) Alzheimer's Disease. New England Journal of Medicine 362: 329–344. - PubMed
-
- Younkin SG (1998) The role of Aβ42 in Alzheimer's disease. Journal of Physiology-Paris 92: 289–292. - PubMed
-
- Wiltfang J, Esselmann H, Bibl M, Smirnov A, Otto M, et al. (2002) Highly conserved and disease-specific patterns of carboxyterminally truncated Aβ peptides 1–37/38/39 in addition to 1–40/42 in Alzheimer's disease and in patients with chronic neuroinflammation. Journal of Neurochemistry 81: 481–496. - PubMed
-
- Meyer-Luehmann M, Stalder M, Herzig MC, Kaeser SA, Kohler E, et al. (2003) Extracellular amyloid formation and associated pathology in neural grafts. Nat Neurosci 6: 370–377. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

