Development of phonological constancy: 19-month-olds, but not 15-month-olds, identify words in a non-native regional accent
- PMID: 23521607
- PMCID: PMC4046279
- DOI: 10.1111/cdev.12087
Development of phonological constancy: 19-month-olds, but not 15-month-olds, identify words in a non-native regional accent
Abstract
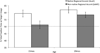
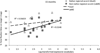
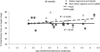
By 12 months, children grasp that a phonetic change to a word can change its identity (phonological distinctiveness). However, they must also grasp that some phonetic changes do not (phonological constancy). To test development of phonological constancy, sixteen 15-month-olds and sixteen 19-month-olds completed an eye-tracking task that tracked their gaze to named versus unnamed images for familiar words spoken in their native (Australian) and an unfamiliar non-native (Jamaican) regional accent of English. Both groups looked longer at named than unnamed images for Australian pronunciations, but only 19-month-olds did so for Jamaican pronunciations, indicating that phonological constancy emerges by 19 months. Vocabulary size predicted 15-month-olds' identifications for the Jamaican pronunciations, suggesting vocabulary growth is a viable predictor for phonological constancy development.
© 2013 The Authors. Child Development © 2013 Society for Research in Child Development, Inc.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Development of phonological constancy: toddlers' perception of native- and Jamaican-accented words.Psychol Sci. 2009 May;20(5):539-42. doi: 10.1111/j.1467-9280.2009.02327.x. Epub 2009 Apr 2. Psychol Sci. 2009. PMID: 19368700 Free PMC article.
-
Delayed development of phonological constancy in toddlers at family risk for dyslexia.Infant Behav Dev. 2019 Nov;57:101327. doi: 10.1016/j.infbeh.2019.101327. Epub 2019 Jun 20. Infant Behav Dev. 2019. PMID: 31207365
-
Navigating accent variability: 24-month-olds recognize known words spoken in an unfamiliar accent but require additional support to learn new words.Infant Behav Dev. 2024 Sep;76:101962. doi: 10.1016/j.infbeh.2024.101962. Epub 2024 May 30. Infant Behav Dev. 2024. PMID: 38820860
-
Infant speech perception bootstraps word learning.Trends Cogn Sci. 2005 Nov;9(11):519-27. doi: 10.1016/j.tics.2005.09.003. Epub 2005 Oct 3. Trends Cogn Sci. 2005. PMID: 16202639 Review.
-
Impacts of acoustic-phonetic variability on perceptual development for spoken language: A review.Wiley Interdiscip Rev Cogn Sci. 2021 Sep;12(5):e1558. doi: 10.1002/wcs.1558. Epub 2021 Mar 3. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Cogn Sci. 2021. PMID: 33660418 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Indexical and linguistic processing by 12-month-olds: Discrimination of speaker, accent and vowel differences.PLoS One. 2017 May 17;12(5):e0176762. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0176762. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28520762 Free PMC article.
-
The iPad as a Research Tool for the Understanding of English Plurals by English, Chinese, and Other L1 Speaking 3- and 4-Year-Olds.Front Psychol. 2016 Nov 22;7:1773. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2016.01773. eCollection 2016. Front Psychol. 2016. PMID: 27920732 Free PMC article.
-
Infant perceptual development for faces and spoken words: an integrated approach.Dev Psychobiol. 2014 Nov;56(7):1454-81. doi: 10.1002/dev.21243. Epub 2014 Aug 4. Dev Psychobiol. 2014. PMID: 25132626 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Two-year-olds interpret novel phonological neighbors as familiar words.Dev Psychol. 2016 Jul;52(7):1011-23. doi: 10.1037/dev0000114. Dev Psychol. 2016. PMID: 27337510 Free PMC article.
-
Preschoolers benefit from sentential context in familiar- and unfamiliar-accented speech.Dev Sci. 2024 Sep;27(5):e13508. doi: 10.1111/desc.13508. Epub 2024 Apr 14. Dev Sci. 2024. PMID: 38616615
References
-
- Best CT. The emergence of native-language phonological influences in infants: A perceptual assimilation model. In: Goodman J, Nusbaum HC, editors. Development of speech perception: The transition from speech sounds to spoken words. Cambridge: MIT Press; 1994. pp. 167–224.
-
- Best CT. A direct realist perspective on cross-language speech perception. In: Strange W, Jenkins JJ, editors. Speech perception and linguistic experience: Issues in cross-language research. Timonium, MD: York Press; 1995. pp. 171–204.
-
- Best CT, Tyler MD, Kitamura C, Bundgaard-Nielsen RL. Presented at the International Conference on Infant Studies. Baltimore, Maryland: 2010. Vocabulary size at 17 months and the emergence of phonological constancy in word recognition across native and nonnative dialects.
-
- Best CT, Tyler MD, Kitamura C, Notley A, Bundgaard-Nielsen RL. Presented at the International Conference on Infant Studies. Vancouver, Canada: 2008. Phonetic specificity of early words? Australian toddlers’ perception of Australian versus Jamaican English pronunciations.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

