Determinants of health literacy and health behavior regarding infectious respiratory diseases: a pathway model
- PMID: 23521806
- PMCID: PMC3621712
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2458-13-261
Determinants of health literacy and health behavior regarding infectious respiratory diseases: a pathway model
Abstract
Background: Health literacy has been defined as the degree to which individuals have the capacity to obtain, process, and understand the basic health information and services needed to make appropriate health decisions. Currently, few studies have validated the causal pathways of determinants of health literacy through the use of statistical modeling. The purpose of the present study was to develop and validate a health literacy model at an individual level that could best explain the determinants of health literacy and the associations between health literacy and health behaviors even health status.
Methods: Skill-based health literacy test and a self-administrated questionnaire survey were conducted among 3222 Chinese adult residents. Path analysis was applied to validate the model.
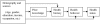
Results: The model explained 38.6% of variance for health literacy, 11.7% for health behavior and 2.3% for health status: (GFI = 0.9990; RMR = 0.0521; χ(2) = 10.2151, P = 0.1159). Education has positive and direct effect on prior knowledge (β = 0.324) and health literacy (β = 0.346). Health literacy is also affected by prior knowledge (β = 0.245) and age (β = -0.361). Health literacy is a direct influencing factor of health behavior (β = 0.101). The most important factor of health status is age (β = 0.107). Health behavior and health status have a positive interaction effect.
Conclusion: This model explains the determinants of health literacy and the associations between health literacy and health behaviors well. It could be applied to develop intervention strategies to increase individual health literacy, and then to promote health behavior and health status.
Figures
References
-
- Ratzan SC, Parker RM. Introduction, in National Library of Medicine current bibliographies in medicine:Health literacy, M.X. C. R. Selden, S. C. Ratzan,& R. M. Parker Editor. Bethesda: NLM Pub; 2000.
-
- Berkman ND, Davis TC, McCormack L. Health Literacy: What Is It? J Health Commun. 2010;15(Suppl 2):9–19. - PubMed
-
- Baur C. New Directions in Research on Public Health and Health Literacy. J Health Commun. 2010;15(Suppl 2):42–50. - PubMed
-
- Paasche-Orlow MK, Wilson EAH, McCormack L. The Evolving Field of Health Literacy Research. J Health Commun. 2010;15(Suppl 2):5–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical