Sccmec type II gene is common among clinical isolates of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in Jakarta, Indonesia
- PMID: 23522081
- PMCID: PMC3637602
- DOI: 10.1186/1756-0500-6-110
Sccmec type II gene is common among clinical isolates of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in Jakarta, Indonesia
Abstract
Background: Community Acquired Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (CA-MRSA) is a strain of MRSA that can cause infections in patients in the community, in which these patients had no previous risk factors for MRSA infection and the patient received 72 hours prior to infection when admitted to hospital. This study aims to determine and compare the characteristics of epidemiological, clinical, and molecular biology of CA-MRSA with HA-MRSA.
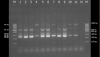
Methods: A total of 11 clinical strains of Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) and Methicillin-sensitive Stapylococcus aureus (MSSA) were collected from 2 hospitals in Jakarta, Indonesia in 2012. SCCmec typing was performed by multiplex polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and the presence of six genes (vraR, vraG, vraA, vraF,fruA, and fruB) associated with vancomycin resistance was examined by simple PCR analysis.
Results: We found three strains of community-acquired MRSA with SCCmec type II and one strain of hospital-acquired MRSA with SCCmec type IV. The other seven strains did not contain mecA genes and SCCmec. Plasmid pUB110 was found in one strain of community-acquired MRSA and two strains of hospital-acquired MRSA. vraA genes were present in 9 of the 11 strains, vraF in 4, vraG in 5, and vraR in 4. Note worthily, three quarters of strains without pUB110 contained vraR and vraF, and 70% contained vraA, whereas 60% of strains with pUB110 contained vraG.
Conclusion: Based on these results, we should be concerned about the possibility of transition from MRSA strains sensitive to vancomycin in VISA strains of MRSA strains obtained in clinical trials. But first we need to look the existence of natural VISA or hVISA among these MRSA strains.
Figures
Similar articles
-
SCCmec typing and detection of VISA-related genes in methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus clinical strains from Kobe University Hospital, Japan.Southeast Asian J Trop Med Public Health. 2006 Nov;37(6):1149-55. Southeast Asian J Trop Med Public Health. 2006. PMID: 17333768
-
Molecular characterization and antibiotic resistance of clinical isolates of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus obtained from Southeast of Iran (Kerman).APMIS. 2014 May;122(5):405-11. doi: 10.1111/apm.12158. Epub 2013 Sep 6. APMIS. 2014. PMID: 24033803
-
Antimicrobial susceptibility and molecular typing of MRSA in cystic fibrosis.Pediatr Pulmonol. 2014 Mar;49(3):230-7. doi: 10.1002/ppul.22815. Epub 2013 Jun 14. Pediatr Pulmonol. 2014. PMID: 23765686
-
[Staphylococcus aureus and antibiotic resistance].Mikrobiyol Bul. 2011 Jul;45(3):565-76. Mikrobiyol Bul. 2011. PMID: 21935792 Review. Turkish.
-
The evolution of Staphylococcus aureus.Infect Genet Evol. 2008 Dec;8(6):747-63. doi: 10.1016/j.meegid.2008.07.007. Epub 2008 Jul 29. Infect Genet Evol. 2008. PMID: 18718557 Review.
Cited by
-
Quantitative proteomic view associated with resistance to clinically important antibiotics in Gram-positive bacteria: a systematic review.Front Microbiol. 2015 Aug 11;6:828. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2015.00828. eCollection 2015. Front Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 26322035 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparison of the Staphylococcal Chromosome Cassette (SCC) mec in Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) and Non-aureus Staphylococci (MRNAS) from Animals and Humans.Antibiotics (Basel). 2021 Mar 4;10(3):256. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics10030256. Antibiotics (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33806351 Free PMC article.
-
Diversity and Dissemination of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) Genotypes in Southeast Asia.Trop Med Infect Dis. 2022 Dec 13;7(12):438. doi: 10.3390/tropicalmed7120438. Trop Med Infect Dis. 2022. PMID: 36548693 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Plasmid profiles among some ESKAPE pathogens in a tertiary care centre in south India.Indian J Med Res. 2019 Feb;149(2):222-231. doi: 10.4103/ijmr.IJMR_2098_17. Indian J Med Res. 2019. PMID: 31219087 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Shore AC, Deasy EC, Slickers P, Brennan G, O’Connell B, Monecke S, Ehricht R, Coleman DC. Detection of staphylococcal cassette chromosome mec type XI carrying highly divergent mecA, mecI, mecR1, blaZ, and ccr genes in human clinical isolates of clonal complex 130 methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2011;55(8):3765–3773. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00187-11. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Reinert RR, Low DE, Rossi F, Zhang X, Wattal C, Dowzicky MJ. Antimicrobial susceptibility among organisms from the Asia/Pacific Rim, Europe and Latin and North America collected as part of TEST and the in vitro activity of tigecycline. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2007;60(5):1018–1029. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkm310. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Aires de Sousa M, Crisostomo MI, Sanches IS, Wu JS, Fuzhong J, Tomasz A, de Lencastre H. Frequent recovery of a single clonal type of multidrug-resistant Staphylococcus aureus from patients in two hospitals in Taiwan and China. J Clin Microbiol. 2003;41(1):159–163. doi: 10.1128/JCM.41.1.159-163.2003. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lee K, Chang CL, Lee NY, Kim HS, Hong KS, Cho HC. Korean nationwide surveillance of antimicrobial resistance of bacteria in 1998. Yonsei Med J. 2000;41(4):497–506. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous