A new unique form of microRNA from human heart, microRNA-499c, promotes myofibril formation and rescues cardiac development in mutant axolotl embryos
- PMID: 23522091
- PMCID: PMC3623845
- DOI: 10.1186/1423-0127-20-20
A new unique form of microRNA from human heart, microRNA-499c, promotes myofibril formation and rescues cardiac development in mutant axolotl embryos
Abstract
Background: A recessive mutation "c" in the Mexican axolotl, Ambystoma mexicanum, results in the failure of normal heart development. In homozygous recessive embryos, the hearts do not have organized myofibrils and fail to beat. In our previous studies, we identified a noncoding Myofibril-Inducing RNA (MIR) from axolotls which promotes myofibril formation and rescues heart development.
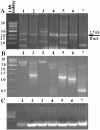
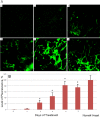
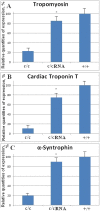
Results: We randomly cloned RNAs from fetal human heart. RNA from clone #291 promoted myofibril formation and induced heart development of mutant axolotls in organ culture. This RNA induced expression of cardiac markers in mutant hearts: tropomyosin, troponin and α-syntrophin. This cloned RNA matches in partial sequence alignment to human microRNA-499a and b, although it differs in length. We have concluded that this cloned RNA is unique in its length, but is still related to the microRNA-499 family. We have named this unique RNA, microRNA-499c. Thus, we will refer to this RNA derived from clone #291 as microRNA-499c throughout the rest of the paper.
Conclusions: This new form, microRNA-499c, plays an important role in cardiac development.
Figures

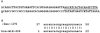

References
-
- Zhang C, Dube DK, Huang X, Zajdel RW, Bhatia R, Foster D, Lemanski SL, Lemanski LF. A point mutation in bioactive RNA results in the failure of mutant heart correction in Mexican axolotls. Anat Embryol. 2003;206:495–506. - PubMed
-
- Rueda-de-León E, Kochegarov A, Lian W, Athauda G, Zhang C, Maier J, Huang X, Achary MP, Moses A, Meyer J, Arms JD, Burlbaw SR, Lemanski SL, Lemanski LF. Human Heart RNA Promotes Tropomyosin Synthesis and Myofibrillogenesis in Mutant Axolotl Hearts. MD-Med Data. 2011;3:223–227.
-
- Wilson KD, Hu S, Venkatasubrahmanyam S, Fu JD, Sun N, Abilez OJ, Baugh JJ, Jia F, Ghosh Z, Li RA, Butte AJ, Wu JC. Dynamic microRNA expression programs during cardiac differentiation of human embryonic stem cells: role for miR-499. Circ Cardiovasc Genet. 2010;3:426–435. doi: 10.1161/CIRCGENETICS.109.934281. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hosoda T, Zheng H, Cabral-da-Silva M, Sanada F, Ide-Iwata N, Ogórek B, Ferreira-Martins J, Arranto C, D’Amario D, del Monte F, Urbanek K, D’Alessandro DA, Michler RE, Anversa P, Rota M, Kajstura J, Leri A. Human cardiac stem cell differentiation is regulated by a mircrine mechanism. Circ. 2011;123:1287–1296. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.110.982918. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

