Functional disruption of macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF) suppresses proliferation of human H460 lung cancer cells by caspase-dependent apoptosis
- PMID: 23522304
- PMCID: PMC3695853
- DOI: 10.1186/1475-2867-13-28
Functional disruption of macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF) suppresses proliferation of human H460 lung cancer cells by caspase-dependent apoptosis
Erratum in
-
Correction: Functional disruption of macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF) suppresses proliferation of human h460 lung cancer cells by caspase-dependent apoptosis.Cancer Cell Int. 2013 Aug 20;13(1):84. doi: 10.1186/1475-2867-13-84. Cancer Cell Int. 2013. PMID: 23961718 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Background: Macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF) is important in regulating cell proliferation and apoptosis in both normal and cancerous cells, and may be important in cancer progression and metastasis. In human non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), the underlying mechanisms responsible for MIF-dependent regulation of cellular proliferation, and cell death remain poorly appreciated.
Methods: The human H460 lung cancer cell-line was treated with an optimally determined dose of 50 pmol/ml MIF siRNA, following which cell proliferation, cell cycle and apoptosis were analyzed. Additionally, known pathways of apoptosis including expression of Annexin-V, enhanced production of caspases-3 and -4 and expression of the Akt signaling protein were assessed in an attempt to provide insights into the signaling pathways involved in apoptosis following disruption of MIF expression.
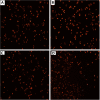
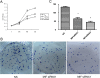
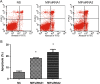
Results: Specific siRNA sequences markedly decreased MIF expression in H460 cells by 2 to 5-fold as compared with the negative control. Moreover, MIF miRNA dampened not only cellular proliferation, but increased the frequency of apoptotic cells as assessed by cell-surface Annexin-V expression. Entry of cells into apoptosis was partly dependent on enhanced production of caspases -3 and -4 while not affecting the expression of either caspase-8 or the Akt signaling pathway.
Conclusions: In a model of NSCLC, knockdown of MIF mRNA expression dampened H460 proliferation by mechanisms partly dependent on entry of cells into apoptosis and enhanced production of caspase-3 and -4. MIF expression may thus be important in NSCLC progression. Targeting MIF may have clinical utility in the management of human lung cancer.
Figures


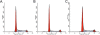

Similar articles
-
Effect and molecular mechanism of mir-146a on proliferation of lung cancer cells by targeting and regulating MIF gene.Asian Pac J Trop Med. 2016 Aug;9(8):806-11. doi: 10.1016/j.apjtm.2016.06.001. Epub 2016 Jun 28. Asian Pac J Trop Med. 2016. PMID: 27569893
-
Correction: Functional disruption of macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF) suppresses proliferation of human h460 lung cancer cells by caspase-dependent apoptosis.Cancer Cell Int. 2013 Aug 20;13(1):84. doi: 10.1186/1475-2867-13-84. Cancer Cell Int. 2013. PMID: 23961718 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Macrophage migration inhibitory factor promotes Warburg effect via activation of the NF‑κB/HIF‑1α pathway in lung cancer.Int J Mol Med. 2018 Feb;41(2):1062-1068. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2017.3277. Epub 2017 Nov 22. Int J Mol Med. 2018. PMID: 29207023
-
Effect of microRNA-135a on Cell Proliferation, Migration, Invasion, Apoptosis and Tumor Angiogenesis Through the IGF-1/PI3K/Akt Signaling Pathway in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017;42(4):1431-1446. doi: 10.1159/000479207. Epub 2017 Jul 17. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017. PMID: 28715819
-
Macrophage migration inhibitory factor as a potential prognostic factor in gastric cancer.World J Gastroenterol. 2015 Sep 14;21(34):9916-26. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i34.9916. World J Gastroenterol. 2015. PMID: 26379396 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Prognostic role of macrophage migration inhibitory factor expression in patients with squamous cell carcinoma of the lung.Thorac Cancer. 2019 Dec;10(12):2209-2217. doi: 10.1111/1759-7714.13198. Epub 2019 Oct 10. Thorac Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31602798 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of Macrophage Migration Inhibitory Factor by a Chimera of Two Allosteric Binders.ACS Med Chem Lett. 2019 Nov 19;11(10):1843-1847. doi: 10.1021/acsmedchemlett.9b00351. eCollection 2020 Oct 8. ACS Med Chem Lett. 2019. PMID: 33062162 Free PMC article.
-
Association of Polymorphisms in Inflammation Genes With the Prognosis of Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients Receiving Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors.Front Oncol. 2022 Mar 18;12:836117. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.836117. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35372081 Free PMC article.
-
Macrophage migration inhibitory factor: Exploring physiological roles and comparing health benefits against oncogenic and autoimmune risks (Review).Int J Mol Med. 2025 Oct;56(4):149. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2025.5590. Epub 2025 Jul 19. Int J Mol Med. 2025. PMID: 40682854 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hallmarks of Cancer Affected by the MIF Cytokine Family.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Jan 6;15(2):395. doi: 10.3390/cancers15020395. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36672343 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

