Foxg1 coordinates the switch from nonradially to radially migrating glutamatergic subtypes in the neocortex through spatiotemporal repression
- PMID: 23523356
- PMCID: PMC3648982
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2013.02.023
Foxg1 coordinates the switch from nonradially to radially migrating glutamatergic subtypes in the neocortex through spatiotemporal repression
Abstract
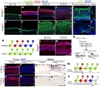
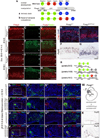
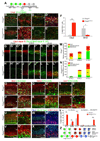
The specification of neuronal subtypes in the cerebral cortex proceeds in a temporal manner; however, the regulation of the transitions between the sequentially generated subtypes is poorly understood. Here, we report that the forkhead box transcription factor Foxg1 coordinates the production of neocortical projection neurons through the global repression of a default gene program. The delayed activation of Foxg1 was necessary and sufficient to induce deep-layer neurogenesis, followed by a sequential wave of upper-layer neurogenesis. A genome-wide analysis revealed that Foxg1 binds to mammalian-specific noncoding sequences to repress over 12 transcription factors expressed in early progenitors, including Ebf2/3, Dmrt3, Dmrta1, and Eya2. These findings reveal an unexpected prolonged competence of progenitors to initiate corticogenesis at a progressed stage during development and identify Foxg1 as a critical initiator of neocorticogenesis through spatiotemporal repression, a system that balances the production of nonradially and radially migrating glutamatergic subtypes during mammalian cortical expansion.
Copyright © 2013 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures




References
-
- Ahlgren S, Vogt P, Bronner-Fraser M. Excess FoxG1 causes overgrowth of the neural tube. J. Neurobiol. 2003;57:337–349. - PubMed
-
- Alcamo E, Chirivella L, Dautzenberg M, Dobreva G, Farinas I, Grosschedl R, McConnell S. Satb2 regulates callosal projection neuron identity in the developing cerebral cortex. Neuron. 2008;57:364–377. - PubMed
-
- Angevine JB, Jr, Sidman RL. Autoradiographic study of cell migration during histogenesis of cerebral cortex in the mouse. Nature. 1961;192:766–768. - PubMed
-
- Arlotta P, Molyneaux B, Chen J, Inoue J, Kominami R, Macklis J. Neuronal subtype-specific genes that control corticospinal motor neuron development in vivo. Neuron. 2005;45:207–221. - PubMed
-
- Bielle F, Griveau A, Narboux-Neme N, Vigneau S, Sigrist M, Arber S, Wassef M, Pierani A. Multiple origins of Cajal-Retzius cells at the borders of the developing pallium. Nat. Neurosci. 2005;8:1002–1012. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

