Rac1 and Cdc42 GTPases regulate shear stress-driven β-catenin signaling in osteoblasts
- PMID: 23524265
- PMCID: PMC3648988
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2013.03.020
Rac1 and Cdc42 GTPases regulate shear stress-driven β-catenin signaling in osteoblasts
Abstract
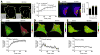
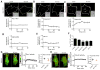
Beta-catenin-dependent TCF/LEF (T-cell factor/lymphocyte enhancing factor) is known to be mechanosensitive and an important regulator for promoting bone formation. However, the functional connection between TCF/LEF activity and Rho family GTPases is not well understood in osteoblasts. Herein we investigated the molecular mechanisms underlying oscillatory shear stress-induced TCF/LEF activity in MC3T3-E1 osteoblast cells using live cell imaging. We employed fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET)-based and green fluorescent protein (GFP)-based biosensors, which allowed us to monitor signal transduction in living cells in real time. Oscillatory (1Hz) shear stress (10 dynes/cm2) increased TCF/LEF activity and stimulated translocation of β-catenin to the nucleus with the distinct activity patterns of Rac1 and Cdc42. The shear stress-induced TCF/LEF activity was blocked by the inhibition of Rac1 and Cdc42 with their dominant negative mutants or selective drugs, but not by a dominant negative mutant of RhoA. In contrast, constitutively active Rac1 and Cdc42 mutants caused a significant enhancement of TCF/LEF activity. Moreover, activation of Rac1 and Cdc42 increased the basal level of TCF/LEF activity, while their inhibition decreased the basal level. Interestingly, disruption of cytoskeletal structures or inhibition of myosin activity did not significantly affect shear stress-induced TCF/LEF activity. Although Rac1 is reported to be involved in β-catenin in cancer cells, the involvement of Cdc42 in β-catenin signaling in osteoblasts has not been identified. Our findings in this study demonstrate that both Rac1 and Cdc42 GTPases are critical regulators in shear stress-driven β-catenin signaling in osteoblasts.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


Similar articles
-
RhoA GTPase interacts with beta-catenin signaling in clinorotated osteoblasts.J Bone Miner Metab. 2013 Sep;31(5):520-32. doi: 10.1007/s00774-013-0449-6. Epub 2013 Mar 26. J Bone Miner Metab. 2013. PMID: 23529802 Free PMC article.
-
Cross-talk between Rac1 GTPase and dysregulated Wnt signaling pathway leads to cellular redistribution of beta-catenin and TCF/LEF-mediated transcriptional activation.Oncogene. 2004 Oct 28;23(50):8260-71. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1208007. Oncogene. 2004. PMID: 15377999
-
Regulation by afadin of cyclical activation and inactivation of Rap1, Rac1, and RhoA small G proteins at leading edges of moving NIH3T3 cells.J Biol Chem. 2009 Sep 4;284(36):24595-609. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.016436. Epub 2009 Jul 9. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19589776 Free PMC article.
-
The role of Rho GTPases' substrates Rac and Cdc42 in osteoclastogenesis and relevant natural medicinal products study.Biosci Rep. 2020 Jul 31;40(7):BSR20200407. doi: 10.1042/BSR20200407. Biosci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32578854 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of Rho family GTPases by cell-cell and cell-matrix adhesion.Biol Res. 2002;35(2):239-46. doi: 10.4067/s0716-97602002000200016. Biol Res. 2002. PMID: 12415742 Review.
Cited by
-
P18: Novel Anticancer Peptide from Induced Tumor-Suppressing Cells Targeting Breast Cancer and Bone Metastasis.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Jun 15;16(12):2230. doi: 10.3390/cancers16122230. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38927935 Free PMC article.
-
RhoGTPases as key players in mammalian cell adaptation to microgravity.Biomed Res Int. 2015;2015:747693. doi: 10.1155/2015/747693. Epub 2015 Jan 29. Biomed Res Int. 2015. PMID: 25649831 Free PMC article. Review.
-
miR-29a Negatively Affects Glucose-Stimulated Insulin Secretion and MIN6 Cell Proliferation via Cdc42/β-Catenin Signaling.Int J Endocrinol. 2019 Aug 28;2019:5219782. doi: 10.1155/2019/5219782. eCollection 2019. Int J Endocrinol. 2019. PMID: 31662747 Free PMC article.
-
Tumour-derived exosomal lncRNA-SOX2OT promotes bone metastasis of non-small cell lung cancer by targeting the miRNA-194-5p/RAC1 signalling axis in osteoclasts.Cell Death Dis. 2021 Jul 2;12(7):662. doi: 10.1038/s41419-021-03928-w. Cell Death Dis. 2021. PMID: 34215717 Free PMC article.
-
The cytoskeleton and connected elements in bone cell mechano-transduction.Bone. 2021 Aug;149:115971. doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2021.115971. Epub 2021 Apr 21. Bone. 2021. PMID: 33892173 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Yokota H, Leong DJ, Sun HB. Mechanical loading: bone remodeling and cartilage maintenance. Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2011;9:237–242. - PubMed
-
- Huang C, Ogawa R. Mechanotransduction in bone repair and regeneration. FASEB J. 2010;24:3625–3632. - PubMed
-
- Rubin CT, Lanyon LE. Regulation of bone formation by applied dynamic loads. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1984;66:397–402. - PubMed
-
- Lang T, LeBlanc A, Evans H, Lu Y, Genant H, Yu A. Cortical and trabecular bone mineral loss from the spine and hip in long-duration spaceflight. Journal of Bone and Mineral Research. 2004;19:1006–1012. - PubMed
-
- Minear S, Leucht P, Jiang J, Liu B, Zeng A, Fuerer C, Nusse R, Helms JA. Wnt proteins promote bone regeneration. Sci Transl Med. 2010;2:29ra30. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

