Long-term reduction in implicit race bias: A prejudice habit-breaking intervention
- PMID: 23524616
- PMCID: PMC3603687
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jesp.2012.06.003
Long-term reduction in implicit race bias: A prejudice habit-breaking intervention
Abstract
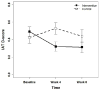
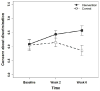
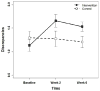
We developed a multi-faceted prejudice habit-breaking intervention to produce long-term reductions in implicit race bias. The intervention is based on the premise that implicit bias is like a habit that can be reduced through a combination of awareness of implicit bias, concern about the effects of that bias, and the application of strategies to reduce bias. In a 12-week longitudinal study, people who received the intervention showed dramatic reductions in implicit race bias. People who were concerned about discrimination or who reported using the strategies showed the greatest reductions. The intervention also led to increases in concern about discrimination and personal awareness of bias over the duration of the study. People in the control group showed none of the above effects. Our results raise the hope of reducing persistent and unintentional forms of discrimination that arise from implicit bias.
Keywords: implicit bias; intervention; prejudice; reduction; self-regulation; stereotyping.
Figures

References
-
- Bargh J. The cognitive monster: The case against the controllability of automatic stereotype effects. In: Chaiken S, Trope Y, editors. Dual-process theories in social psychology. New York: Guilford Press; 1999. pp. 361–382.
-
- Beck AT, Alford BA. Depression: Causes and treatment. 2. Baltimore, MD: University of Pennsylvania Press; 2009.
-
- Bertrand M, Mullainathan S. Are Emily and Greg more employable than Lakisha and Jamal? A field experiment on labor market discrimination. American Economic Review. 2004;94:991–1013. doi: 10.1257/0002828042002561. - DOI
-
- Blair IV. The malleability of automatic stereotypes and prejudice. Personality and Social Psychology Review. 2002;6:242–261. doi: 10.1207/S15327957PSPR0603_8. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
