Detection of galectin-3 interaction with commensal bacteria
- PMID: 23524672
- PMCID: PMC3648028
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.03694-12
Detection of galectin-3 interaction with commensal bacteria
Abstract
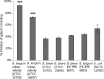
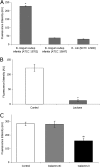
A panel of commensal bacteria was screened for the ability to interact with galectin-3. Two strains of Bifidobacterium longum subsp. infantis interacted to a greater extent than did the pathogenic positive control, Escherichia coli NCTC 12900. Further validation of the interaction was achieved by using agglutination and solid-phase binding assays.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Galacto- and Fructo-oligosaccharides Utilized for Growth by Cocultures of Bifidobacterial Species Characteristic of the Infant Gut.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2020 May 19;86(11):e00214-20. doi: 10.1128/AEM.00214-20. Print 2020 May 19. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32220841 Free PMC article.
-
Broad conservation of milk utilization genes in Bifidobacterium longum subsp. infantis as revealed by comparative genomic hybridization.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2010 Nov;76(22):7373-81. doi: 10.1128/AEM.00675-10. Epub 2010 Aug 27. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2010. PMID: 20802066 Free PMC article.
-
Fucosyllactose and L-fucose utilization of infant Bifidobacterium longum and Bifidobacterium kashiwanohense.BMC Microbiol. 2016 Oct 26;16(1):248. doi: 10.1186/s12866-016-0867-4. BMC Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 27782805 Free PMC article.
-
Prevention of Escherichia coli O157:H7 infection in gnotobiotic mice associated with Bifidobacterium strains.Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 2010 Feb;97(2):107-17. doi: 10.1007/s10482-009-9391-y. Epub 2009 Nov 13. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 2010. PMID: 19911297
-
Proposal to reclassify the three biotypes of Bifidobacterium longum as three subspecies: Bifidobacterium longum subsp. longum subsp. nov., Bifidobacterium longum subsp. infantis comb. nov. and Bifidobacterium longum subsp. suis comb. nov.Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2008 Apr;58(Pt 4):767-72. doi: 10.1099/ijs.0.65319-0. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2008. PMID: 18398167
Cited by
-
Highlights on the Role of Galectin-3 in Colorectal Cancer and the Preventive/Therapeutic Potential of Food-Derived Inhibitors.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Dec 22;15(1):52. doi: 10.3390/cancers15010052. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36612048 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Galectin-3: a novel antimicrobial host factor identified in goat nasal mucus.Vet Res. 2025 Jul 21;56(1):153. doi: 10.1186/s13567-025-01586-w. Vet Res. 2025. PMID: 40696454 Free PMC article.
-
Microbiota-induced S100A11-RAGE axis underlies immune evasion in right-sided colon adenomas and is a therapeutic target to boost anti-PD1 efficacy.Gut. 2025 Jan 17;74(2):214-228. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2024-332193. Gut. 2025. PMID: 39251326 Free PMC article.
-
Engineering of CHO cells for the production of vertebrate recombinant sialyltransferases.PeerJ. 2019 Feb 11;7:e5788. doi: 10.7717/peerj.5788. eCollection 2019. PeerJ. 2019. PMID: 30775162 Free PMC article.
-
Multivalent scaffolds induce galectin-3 aggregation into nanoparticles.Beilstein J Org Chem. 2014 Jul 10;10:1570-7. doi: 10.3762/bjoc.10.162. eCollection 2014. Beilstein J Org Chem. 2014. PMID: 25161713 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gunning AP, Bongaerts RJ, Morris VJ. 2009. Recognition of galactan components of pectin by galectin-3. FASEB J. 23: 415–424 - PubMed
-
- Cao Z, Said N, Amin S, Wu HK, Bruce A, Garate M, Hsu DK, Kuwabara I, Liu FT, Panjwani N. 2002. Galectins-3 and -7, but not galectin-1, play a role in re-epithelialization of wounds. J. Biol. Chem. 277: 42299–42305 - PubMed
-
- Dumic J, Dabelic S, Flogel M. 2006. Galectin-3: an open-ended story. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1760: 616–635 - PubMed
-
- Leffler H, Carlsson S, Hedlund M, Qian Y, Poirier F. 2004. Introduction to galectins. Glycoconj. J. 19: 433–440 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

