The clinicopathologic significance of p53 and BAF-250a (ARID1A) expression in clear cell carcinoma of the endometrium
- PMID: 23524907
- PMCID: PMC3886836
- DOI: 10.1038/modpathol.2013.35
The clinicopathologic significance of p53 and BAF-250a (ARID1A) expression in clear cell carcinoma of the endometrium
Abstract
TP53 mutation (and associated p53 protein overexpression) is probably a negative prognostic marker in endometrial cancers, but its relevance in the rarer histologic subtypes, including clear cell carcinomas, has not been delineated. Preclinical studies suggest functional interactions between p53 and the BAF250a protein, the product of a tumor suppressor gene ARID1A (adenine-thymine (AT)-rich interactive domain containing protein 1A) that is frequently mutated in ovarian clear cell carcinoma. In this study, we evaluated the significance of p53 and BAF250a expression, as assessed by immunohistochemistry, in a group of 50 endometrial clear cell carcinomas. Of 50 cases, 17 (34%) were p53+, and the remaining 33 cases had a p53 wild-type (p53-wt) immunophenotype. Of the 11 relapses/recurrences in the entire data set, 73% were in the p53+ group (P=0.008). On univariate analyses, the median overall survival for the p53-wt patients (83 months) was longer than the p53+ patients (63 months) (P=0.07), and the median progression-free survival for the p53-wt group (88 months) was significantly longer than the p53+ group (56 months) (P=0.01). On multivariate analyses, p53 expression was not associated with reduced overall or progression-free survival. In addition, p53 status was not significantly associated with pathologic stage or morphologic patterns. Of the 50 cases, 10 (20%) showed a complete loss of BAF250a expression. There was no significant correlation between p53 and BAF250a expression. The p53+/BAF250a-, p53+/BAF250a+, p53-wt/BAF250a+ and p53-wt/BAF250a- composite immunophenotypes were identified in 8%, 26%, 54% and 12% of cases, respectively, and neither loss of BAF250a expression nor composite p53/BAF250a expression patterns were associated with reduced overall or progression-free survival. In conclusion, a significant subset of CCC express p53, and these cases are apparently not definable by their morphologic features. P53 expression may be a negative prognostic factor in this histotype, and warrants additional studies. Loss of BAF250a expression has no prognostic significance in endometrial clear cell carcinomas.
Figures
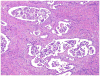




References
-
- Creasman WT, Odicino F, Maisonneuve P, Quinn MA, Beller U, Benedet JL, Heintz AP, Ngan HY, Pecorelli S. Carcinoma of the corpus uteri. FIGO 26th Annual Report on the Results of Treatment in Gynecological Cancer. Int J Gynaecol Obstet. 2006;95 (Suppl 1):S105–43. - PubMed
-
- McMeekin DS, Filiaci VL, Thigpen JT, Gallion HH, Fleming GF, Rodgers WH Gynecologic Oncology Group study. The relationship between histology and outcome in advanced and recurrent endometrial cancer patients participating in first-line chemotherapy trials: a Gynecologic Oncology Group study. Gynecol Oncol. 2007;106:16–22. - PubMed
-
- Olawaiye AB, Boruta DM., 2nd Management of women with clear cell endometrial cancer: a Society of Gynecologic Oncology (SGO) review. Gynecol Oncol. 2009;113:277–83. - PubMed
-
- Fadare O. The Molecular Pathogenesis of Endometrial Clear Cell Carcinoma: Unclear, Uncertain and Possibly Heterogeneous. Expert Review of Obstetrics & Gynecology. 2012;7:109–112.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

