Lymphatic vasculature mediates macrophage reverse cholesterol transport in mice
- PMID: 23524964
- PMCID: PMC3613904
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI63685
Lymphatic vasculature mediates macrophage reverse cholesterol transport in mice
Abstract
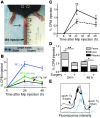
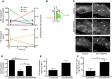
Reverse cholesterol transport (RCT) refers to the mobilization of cholesterol on HDL particles (HDL-C) from extravascular tissues to plasma, ultimately for fecal excretion. Little is known about how HDL-C leaves peripheral tissues to reach plasma. We first used 2 models of disrupted lymphatic drainage from skin--1 surgical and the other genetic--to quantitatively track RCT following injection of [3H]-cholesterol-loaded macrophages upstream of blocked or absent lymphatic vessels. Macrophage RCT was markedly impaired in both models, even at sites with a leaky vasculature. Inhibited RCT was downstream of cholesterol efflux from macrophages, since macrophage efflux of a fluorescent cholesterol analog (BODIPY-cholesterol) was not altered by impaired lymphatic drainage. We next addressed whether RCT was mediated by lymphatic vessels from the aortic wall by loading the aortae of donor atherosclerotic Apoe-deficient mice with [2H]6-labeled cholesterol and surgically transplanting these aortae into recipient Apoe-deficient mice that were treated with anti-VEGFR3 antibody to block lymphatic regrowth or with control antibody to allow such regrowth. [2H]-Cholesterol was retained in aortae of anti-VEGFR3-treated mice. Thus, the lymphatic vessel route is critical for RCT from multiple tissues, including the aortic wall. These results suggest that supporting lymphatic transport function may facilitate cholesterol clearance in therapies aimed at reversing atherosclerosis.
Figures



Comment in
-
Lymphatic vessels clean up your arteries.J Clin Invest. 2013 Apr;123(4):1417-9. doi: 10.1172/JCI68657. Epub 2013 Mar 25. J Clin Invest. 2013. PMID: 23524960 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 HL-096539/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- S10 RR027940/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK056341/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL064163/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA091842/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK020579/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- 1S10RR027940MS/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1RR024992/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024992/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA91842/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA109322/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA012197/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL-64163/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 5P30CA12197/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL096539/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000448/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

