Brain and muscle Arnt-like 1 is a key regulator of myogenesis
- PMID: 23525013
- PMCID: PMC3672937
- DOI: 10.1242/jcs.120519
Brain and muscle Arnt-like 1 is a key regulator of myogenesis
Abstract
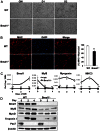
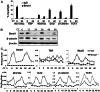
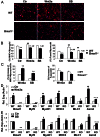
The circadian clock network is an evolutionarily conserved mechanism that imparts temporal regulation to diverse biological processes. Brain and muscle Arnt-like 1 (Bmal1), an essential transcriptional activator of the clock, is highly expressed in skeletal muscle. However, whether this key clock component impacts myogenesis, a temporally regulated event that requires the sequential activation of myogenic regulatory factors, is not known. Here we report a novel function of Bmal1 in controlling myogenic differentiation through direct transcriptional activation of components of the canonical Wnt signaling cascade, a major inductive signal for embryonic and postnatal muscle growth. Genetic loss of Bmal1 in mice leads to reduced total muscle mass and Bmal1-deficient primary myoblasts exhibit significantly impaired myogenic differentiation accompanied by markedly blunted expression of key myogenic regulatory factors. Conversely, forced expression of Bmal1 enhances differentiation of C2C12 myoblasts. This cell-autonomous effect of Bmal1 is mediated by Wnt signaling as both expression and activity of Wnt components are markedly attenuated by inhibition of Bmal1, and activation of the Wnt pathway partially rescues the myogenic defect in Bmal1-deficient myoblasts. We further reveal direct association of Bmal1 with promoters of canonical Wnt pathway genes, and as a result of this transcriptional regulation, Wnt signaling components exhibit intrinsic circadian oscillation. Collectively, our study demonstrates that the core clock gene, Bmal1, is a positive regulator of myogenesis, which may represent a temporal regulatory mechanism to fine-tune myocyte differentiation.
Keywords: Circadian clock; Myogenesis; Wnt signaling.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Brain and muscle Arnt-like 1 promotes skeletal muscle regeneration through satellite cell expansion.Exp Cell Res. 2015 Feb 1;331(1):200-210. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2014.08.041. Epub 2014 Sep 9. Exp Cell Res. 2015. PMID: 25218946
-
The clock gene, brain and muscle Arnt-like 1, regulates adipogenesis via Wnt signaling pathway.FASEB J. 2012 Aug;26(8):3453-63. doi: 10.1096/fj.12-205781. Epub 2012 May 18. FASEB J. 2012. PMID: 22611086 Free PMC article.
-
Targeted screening and identification of chlorhexidine as a pro-myogenic circadian clock activator.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2023 Jul 31;14(1):190. doi: 10.1186/s13287-023-03424-2. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2023. PMID: 37525228 Free PMC article.
-
The functional significance of the skeletal muscle clock: lessons from Bmal1 knockout models.Skelet Muscle. 2016 Oct 13;6:33. doi: 10.1186/s13395-016-0107-5. eCollection 2016. Skelet Muscle. 2016. PMID: 27752300 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Circadian modification network of a core clock driver BMAL1 to harmonize physiology from brain to peripheral tissues.Neurochem Int. 2018 Oct;119:11-16. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2017.12.013. Epub 2018 Jan 3. Neurochem Int. 2018. PMID: 29305918 Review.
Cited by
-
Chrono-Nutrition Has Potential in Preventing Age-Related Muscle Loss and Dysfunction.Front Neurosci. 2021 Apr 16;15:659883. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2021.659883. eCollection 2021. Front Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 33935640 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SRF-MRTF signaling suppresses brown adipocyte development by modulating TGF-β/BMP pathway.Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2020 Sep 15;515:110920. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2020.110920. Epub 2020 Jun 27. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2020. PMID: 32603734 Free PMC article.
-
Adult stem cell maintenance and tissue regeneration around the clock: do impaired stem cell clocks drive age-associated tissue degeneration?Biogerontology. 2018 Dec;19(6):497-517. doi: 10.1007/s10522-018-9772-6. Epub 2018 Oct 29. Biogerontology. 2018. PMID: 30374678 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The contribution of circadian clock to the biological processes.Front Mol Biosci. 2024 Jun 6;11:1387576. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2024.1387576. eCollection 2024. Front Mol Biosci. 2024. PMID: 38903177 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanical Stress Affects Circadian Rhythm in Skeletal Muscle (C2C12 Myoblasts) by Reducing Per/Cry Gene Expression and Increasing Bmal1 Gene Expression.Med Sci Monit. 2021 Jan 14;27:e928359. doi: 10.12659/MSM.928359. Med Sci Monit. 2021. PMID: 33444293 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Andrews J. L., Zhang X., McCarthy J. J., McDearmon E. L., Hornberger T. A., Russell B., Campbell K. S., Arbogast S., Reid M. B., Walker J. R. et al.(2010). CLOCK and BMAL1 regulate MyoD and are necessary for maintenance of skeletal muscle phenotype and function. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 107, 19090–19095 10.1073/pnas.1014523107 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

