Physiologic brain activity causes DNA double-strand breaks in neurons, with exacerbation by amyloid-β
- PMID: 23525040
- PMCID: PMC3637871
- DOI: 10.1038/nn.3356
Physiologic brain activity causes DNA double-strand breaks in neurons, with exacerbation by amyloid-β
Abstract
We show that a natural behavior, exploration of a novel environment, causes DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs) in neurons of young adult wild-type mice. DSBs occurred in multiple brain regions, were most abundant in the dentate gyrus, which is involved in learning and memory, and were repaired within 24 h. Increasing neuronal activity by sensory or optogenetic stimulation increased neuronal DSBs in relevant but not irrelevant networks. Mice transgenic for human amyloid precursor protein (hAPP), which simulate key aspects of Alzheimer's disease, had increased neuronal DSBs at baseline and more severe and prolonged DSBs after exploration. Interventions that suppress aberrant neuronal activity and improve learning and memory in hAPP mice normalized their levels of DSBs. Blocking extrasynaptic NMDA-type glutamate receptors prevented amyloid-β (Aβ)-induced DSBs in neuronal cultures. Thus, transient increases in neuronal DSBs occur as a result of physiological brain activity, and Aβ exacerbates DNA damage, most likely by eliciting synaptic dysfunction.
Figures
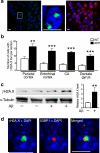
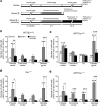
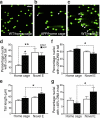
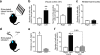
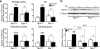

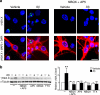
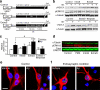
Comment in
-
Breaking news: thinking may be bad for DNA.Nat Neurosci. 2013 May;16(5):518-9. doi: 10.1038/nn.3384. Nat Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23619752 No abstract available.
References
-
- Moreira PI, et al. Nucleic acid oxidation in Alzheimer disease. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2008;44:1493–1505. - PubMed
-
- Lu T, et al. Gene regulation and DNA damage in the ageing human brain. Nature. 2004;429:883–891. - PubMed
-
- Ismail IH, Hendzel MJ. The gamma-H2A.X: Is it just a surrogate marker of double-strand breaks or much more? Environ. Mol. Mutagen. 2008;49:73–82. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

