Oral glucose for pain relief during examination for retinopathy of prematurity: a masked randomized clinical trial
- PMID: 23525316
- PMCID: PMC3584268
- DOI: 10.6061/clinics/2013(02)oa13
Oral glucose for pain relief during examination for retinopathy of prematurity: a masked randomized clinical trial
Abstract
Objective: Ophthalmologic examination for retinopathy of prematurity is a painful procedure. Pharmacological and non-pharmacological interventions have been proposed to reduce pain during eye examinations. This study aims to evaluate the analgesic effect of 25% glucose using a validated pain scale during the first eye examination for retinopathy of prematurity in preterm infants with birth weight <1,500 g and/or gestational age <32 weeks.
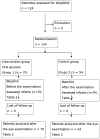
Methods: A masked, randomized clinical trial for one dose of 1 ml of oral 25% glucose solution 2 minutes before the first ophthalmologic examination for retinopathy of prematurity was conducted between March 2008 and April 2010. The results were compared to those of a control group that did not receive oral glucose solution. Pain was evaluated using a Neonatal Infant Pain Scale immediately before and immediately after the ophthalmologic examination in both groups. Clinicaltrials.gov: NCT00648687
Results: One hundred and twenty-four patients who were examined for the first time for retinopathy of prematurity were included. Seventy were included in the intervention group and 54 in the control group. The number of patients with pain immediately before the procedure was similar in both groups. The number of patients with pain after ophthalmologic examination was 15.7% in the intervention group and 68.5% in the control group (p<0.001).
Conclusions: One ml of oral 25% glucose solution given 2 minutes before an ophthalmologic examination for retinopathy of prematurity was an effective measure for pain relief.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported.
Figures
References
-
- Fielder AR, Reynolds JD. Retinopathy of prematurity: clinical aspects. Semin Neonatol. 2001;6(6):461–75. - PubMed
-
- Belda S, Pallas CR, De la Cruz J, Tejada P. Screening for retinopathy of prematurity: is it painful. Biol Neonate. 2004;86(3):195–200. - PubMed
-
- Rush R, Rush S, Ighani F, Anderson B, Irwin M, Naqvi M. The effects of comfort care on the pain response in preterm infants undergoing screening for retinopathy of prematurity. Retina. 2005;25(1):59–62. - PubMed
-
- Rush R, Rush S, Nicolau J, Chapman K, Naqvi M. Systemic manifestations in response to mydriasis and physical examination during screening for retinopathy of prematurity. Retina. 2004;24(2):242–5. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous